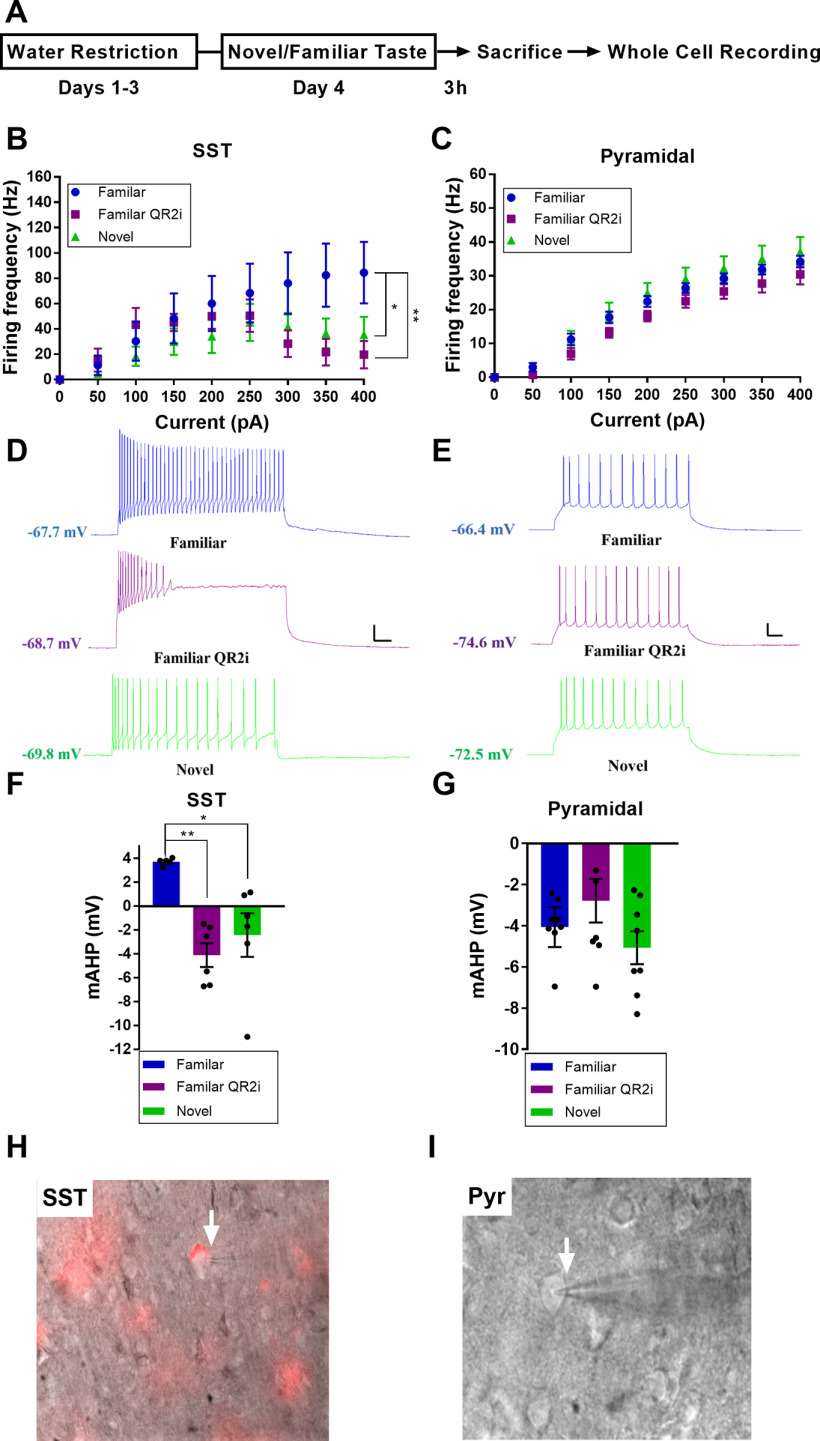
Figure 4.
QR2 suppression reduces SST interneuron excitability and increases mAHP. A, Mice were trained to drink from pipettes and were then given either a novel (saccharin) or familiar (water) taste. The mice were killed 3 h later, at a time QR2 is suppressed following novelty, and whole-cell patch recording was conducted in SST and pyramidal neurons. QR2 inhibitor (QR2i) was added into the recording pipette following familiar taste consumption, to compare with the novel taste group. B, Experience of a novel taste reduces SST interneuron excitability in the aIC 3 h following consumption and QR2 inhibition 3 h following a familiar taste mimics the reduced firing frequency following novelty [two-way repeated measures ANOVA, interaction F(16,120) = 2.707, p < 0.0011; pulse F(8,120) = 12.91, p < 0.0001; groups F(2,15) = 1.526, p = 0.2492; subjects (matching) F(15,120) = 10.88, p < 0.0001; Sidak’s multiple comparisons test of familiar vs familiar QR2i at 300 pA, p = 0. 0.0365; familiar vs familiar QR2i at 350 pA, p = 0. 0.0047, familiar vs novel at 350, p = 0.0576; familiar vs familiar QR2i at 400, p = 0.0023, familiar vs novel at 400, p = 0.0384]. C, Excitatory primary neurons of the aIC show no change in firing frequency 3 h following novel taste consumption or inhibition of QR2 [two-way repeated measures ANOVA, Interaction F(16,192) = 1.102, p < 0.3555; pulse F(8,192) = 269.8, p < 0.0001; groups F(2,24) = 1.873, p = 0.1754; subjects (matching) F(24,192) = 16.95, p < 0.0001]. D, Representative traces from SST interneurons in the aIC. Scale bar: 20 mV (vertical), 50 ms (horizontal) from 350-pA current steps. E, Representative traces from pyramidal neurons in the aIC. Scale bar: 20 mV (vertical), 50 ms (horizontal) from 250-pA current steps. F, Experience of a novel taste increases SST interneuron mAHP in the aIC 3 h following consumption and QR2 inhibition 3 h following a familiar taste mimics the increase in mAHP following novelty (familiar 3.714 ± 0.131 mV, n = 5 cells from n = 3 mice; familiar QR2i −4.103 ± 0.995 mV, n = 6 cells from n = 3 mice; novel −2.425 ± 1.825 mV, n = 6 cells from n = 4 mice; one-way ANOVA, F(2,14) = 9.71, p = 0.0023; Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test, familiar vs familiar QR2i, p = 0.0022; familiar vs novel, p = 0.013; familiar QR2i vs novel, p = 0.6165). G, Experience of a novel taste does not affect pyramidal neuron mAHP in the aIC 3 h following consumption and QR2 inhibition following a familiar taste has no effect on mAHP (familiar −4.063 ± 0.972 mV, n = 10 cells from n = 3 mice; familiar QR2i −2.788 ± 1.053 mV, n = 8 cells from n = 3 mice; novel −5.066 ± 0.799 mV, n = 8 cells from n = 3 mice; one-way ANOVA, F(2,23) = 1.312, p = 0.2887). H, Representative image of mCherry-expressing SST interneuron in the aIC. I, Representative image of pyramidal neuron in the aIC. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005.