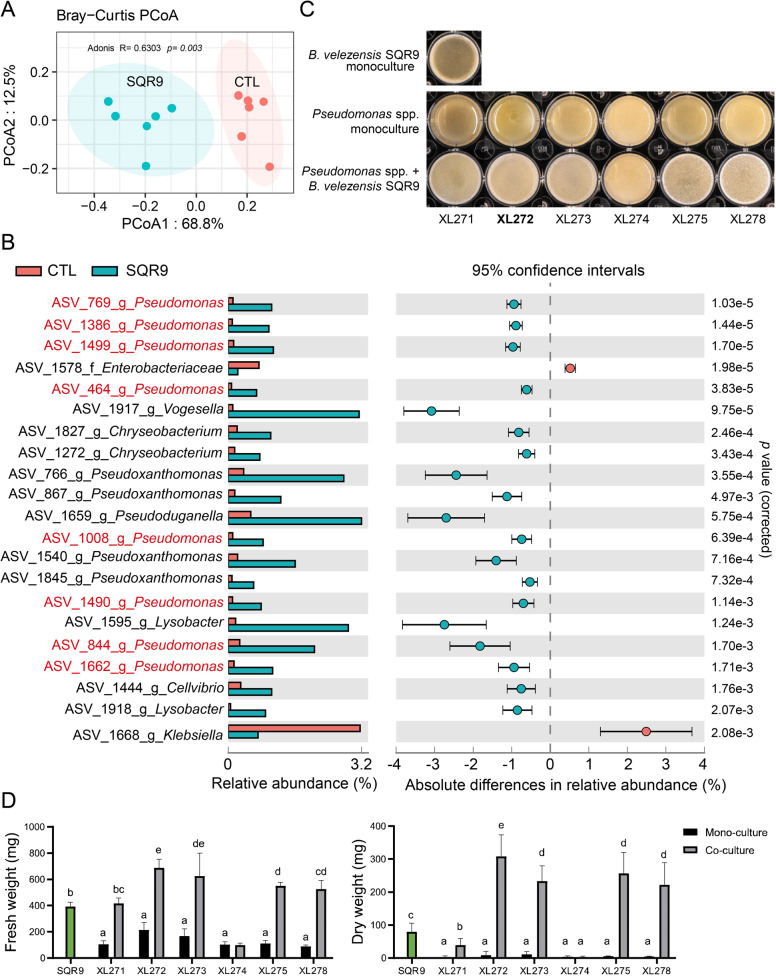
Fig. 1. Influence of B. velezensis SQR9 on rhizosphere microbiota, biofilm phenotype, and quantification of isolated bacteria with predicted synergism.
A Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) of the rhizosphere bacteria community is plotted based on the Bray−Curtis distance metrices for taxonomical data (p < 0.01). Permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) was performed using the adonis function from the vegan R package. Samples were isolated from rhizosphere of untreated control (CTL) and B. velezensis SQR9 inoculated (SQR9) plants (n = 6). B Absolute differences in relative abundance of genera between control (CTL) and B. velezensis SQR9 inoculated (SQR9) rhizosphere samples (Welch’s t test; p < 0.05). ASVs matched to Pseudomonas spp. are marked in red. Error bars represent standard deviations. C Biofilm phenotype of predicted cooperating strains. XL271-278 represents different Pseudomonas isolates. Well diameter is 15.6 mm. D Pellicle biomass quantified by fresh weight and dry weight. SQR9 represent B. velezensis SQR9, XL271-278 represent different Pseudomonas spp. Green bars represent monoculture of B. velezensis SQR9. Coculture means co-cultivated with strain SQR9. Pellicles were cultivated in TSB medium for 24 h. Data presented are the mean ± s.d. (n = 4−6). Significance test was performed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test via Prism 8. Different letters indicate statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences.