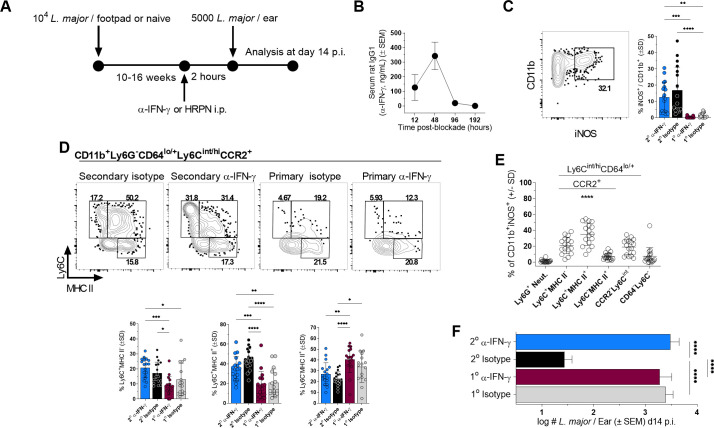
Fig 4. Early availability of IFN-γ is critical for L. major control.
(A-F) Chronic mice (2o) or naïve (1o) AMCs were injected i.p. with 0.5mg anti-IFN-γ or HRPN control 2 hours prior to challenge with 5000 L. major and analysis was conducted on day 14 p.ch. (B) ELISA assessment of serum rat IgG1 (anti-IFN-γ ng/mL) from serum at the indicated time points post-anti-IFN-γ treatment. (C and D) Representative flow plots and frequency of CD11b+ cells expressing the specified phenotypic markers (D, lower panels) or iNOS (C, right panel) in the ear dermis. (E) Phenotype of iNOS+CD11b+ cells at the dermal site of L. major challenge in mice with a chronic primary infection. (F) Parasite loads as determined by LDA. n = 3 (B) or n = 11–18 (C-F). Data is pooled from 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-test (C, D, F). In (E) p<0.00001 versus all other groups.