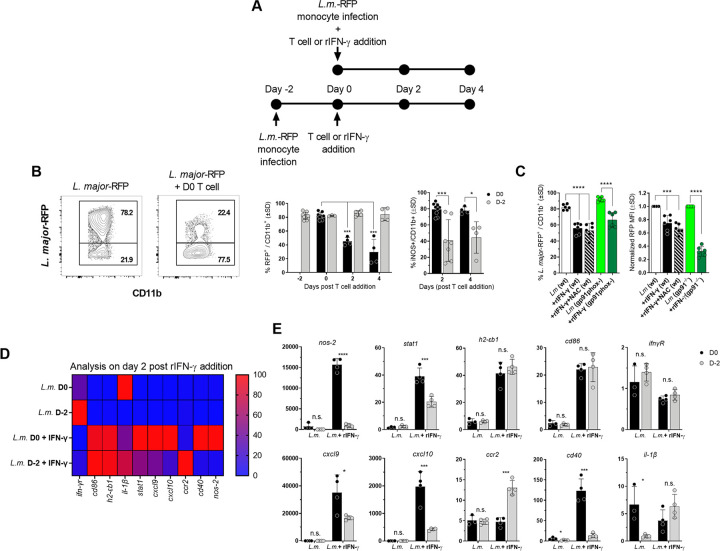
Fig 7. Infected monocytes are refractory to delayed of Th1EFF effector function.
(A) Purified bone marrow-derived primary monocytes were infected with L.m.-RFP, washed, and in-vitro-generated Th1 PEPCK-specific T cells were added immediately after or on day 2 p.i.. Monocytes were assessed at 2 or 4 days post-T cell addition. (B) Representative flow plots of CD11b vs L. major-RFP and frequency of RFP+ infected (left panel) and iNOS+ (right panel) monocytes at 2 or 4 days post-T cell addition. (C) Purified bone marrow-derived primary monocytes from wt or Phox-/- mice were infected with L.m.-RFP. Indicated groups were treated with the ROS inhibitor NAC (N-acetyl-l-cysteine) at the time of infection. Recombinant IFN-γ was added immediately p.i.. Frequency of RFP+ infected monocytes and normalized RFP MFI in infected monocytes is shown. (D) Purified bone marrow-derived primary monocytes were infected with L.m.-RFP and recombinant IFN-γ was added immediately after or on day 2 p.i.. Monocytes gene expression was assessed via qRT-PCR 2 days after IFN-γ addition. Gene expression is shown via heatmap. (E) Individual gene expression between treatment groups. In (B) n = 4–9 representing two pooled experiments. In (C) n = 6 representing two pooled experiments. (D and E) n = 4 mice/group/experiment. Data is representative experiment of two repeat experiments.