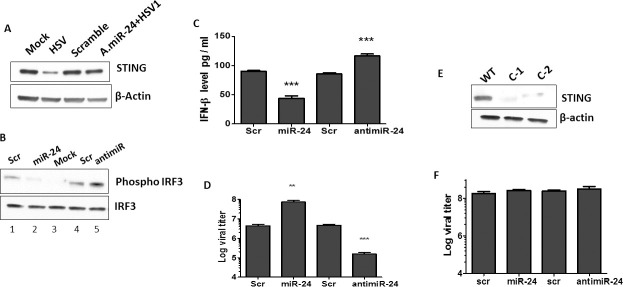
Fig 2. miR-24 promotes HSV1 replication by suppressing STING expression.
(A) HT1080 cells were transfected with Scramble control (lane 3), or antimiR-24 (lane 4). 24 hours later, HSV1 infection was given to antimiR-24 transfected cells (lane4) and STING protein levels were determined after 16 hours post infection. Mock (lane 1) and HSV1 infected HT1080 cells (lane 2) (16hrs post infection) were also analyzed. (B). HT1080 cells were transfected with 1-Scramble control, 2-miR-24, 3-mock control, 4- Scramble for antimiR 5- antimiR-24 and HSV1 infection was given 24 hours post transfection. Phospho-IRF-3 and IRF-3 levels were determined 3 hours post HSV1 infection. (C) HT1080 cells were transfected with 1-Scramble control, 2-miR-24, 3-Scramble control for antimiR or 4-antimiR24. HSV1 infection (MOI-5) was given 24 hours post transfection and Interferon-β protein in culture supernatants was quantified by sandwich ELISA 10 hours post HSV1 infection. (D) HT1080 cells were transfected with 1-Scramble control, 2-miR-24, 3-Scramble control for antimiR or 4-antimiR-24. HSV1 infection was given 24 hours post transfection and viral titer was quantified 12 hours post HSV1 infection. The cells along with culture media was frozen and thawed thrice to determine titer in cells and media. (E) STING expression was analyzed in WT and STING KD HT1080 cells (2 clonal isolates C1 and C2 were analyzed) to confirm knockdown of STING. (F) HT1080 STING knock down cells were transfected with 1-Scramble control, 2-miR-24, 3-Scramble control for antimiR or 4-antimiR-24. HSV1 infection was given 24 hours post transfection and viral titer in cells and culture supernatants was quantified 12 hours post HSV1 infection. (C, D, F: Mean ± SEM, N = 3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.