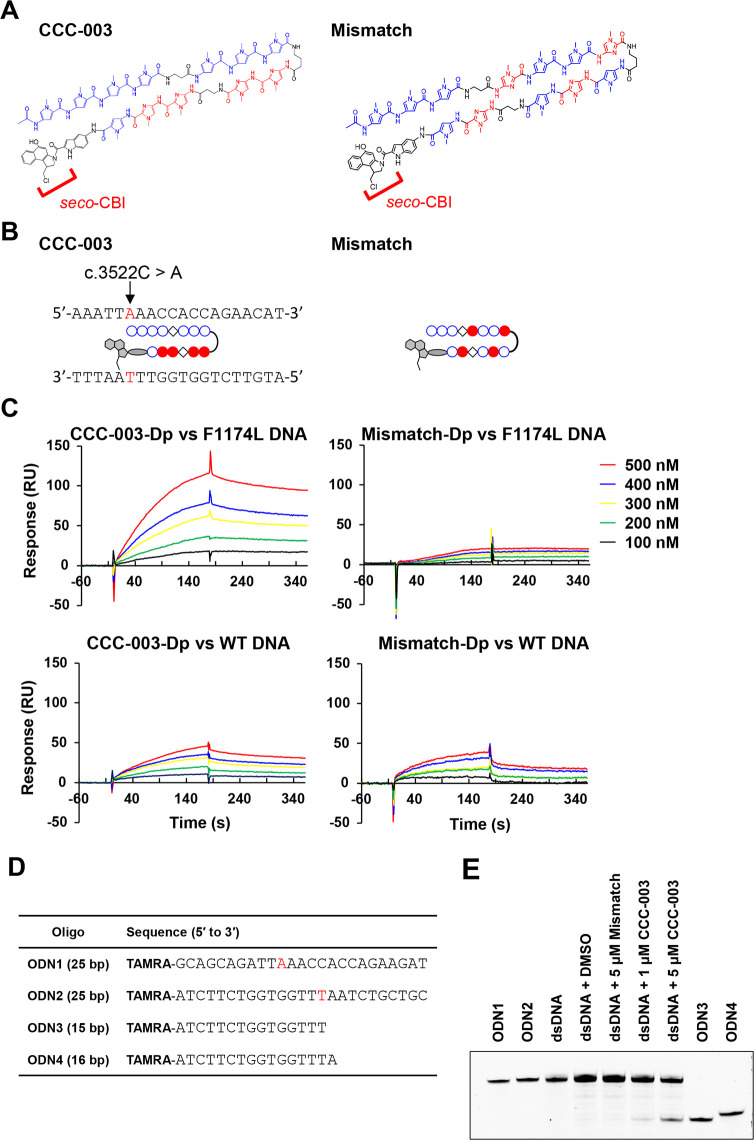
Fig 1. CCC-003 specifically recognizes the DNA sequence of mutant ALK.
(A) Chemical structure of CCC-003, a sequence-specific DNA-alkylating agent directly targeting the F1174L-mutated ALK gene, and the mismatch polyamide (Mismatch), which had no binding motif within the coding region of the ALK gene. The site of alkylation is shown in red. (B) Schematic drawing of CCC-003 and Mismatch at the site of ALK F1174L mutation. Blue open circles represent pyrrole moieties and red circles represent imidazole. Arrow indicates the position of the ALK F1174L mutation. (C) SPR sensorgrams for the interaction of CCC-003-Dp with hairpin DNAs containing the F1174L mutation sequence, Mismatch-Dp with hairpin DNAs containing the F1174L mutation sequence, CCC-003-Dp with hairpin DNAs containing the wild-type sequence, and Mismatch-Dp with hairpin DNAs containing the wild-type sequence. Oligonucleotides were immobilized on the surface of an SA sensor chip. Five curves of the lowest, mid-low, middle, mid-high, and highest concentration of PI polyamide indicate 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 nM, respectively. (D) Oligonucleotides used in PAGE analysis. (E) PAGE analysis confirmed the alkylation site on target DNA fragment by CCC-003. Annealed DNA fragment (dsDNA) using 5′-TAMRA-labeled DNA oligonucleotides (ODN1 and ODN2) was incubated with DMSO, Mismatch polyamide or CCC-003 and heated to visualize alkylated bands by PAGE analysis. The alkylated DNA fragments were analyzed with reference DNAs (ODN3 and ODN4).