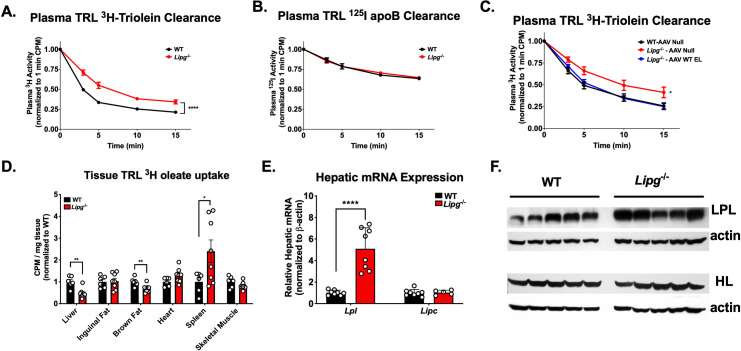
Fig 5. Lipg deficiency delays TRL lipolysis in mice.
A.3H oleate plasma clearance curves from EL WT vs. Lipg-/- mice administered 3H-triolein labeled human TRLs. Mice were administered radiolabeled TRLs and plasma 3H levels were measured over 15 minutes and normalized to the 1 minute timepoint. B. Clearance of 125I tyramine cellobiose labeled human TRLs in EL WT vs. Lipg-/- mice fed a high fat diet for 12 weeks. Plasma clearance of 125I-TRL apolipoprotein B (apoB) after intravenous TRL administration was measured over 15 minutes. C. 3H-triolein-labeled TRL clearance in WT mice treated with AAV Null vector, Lipg-/- mice treated with AAV Null, or Lipg-/- mice treated with AAV expressing murine Lipg and all fed a high-fat diet for 12 weeks and then treated with radiolabeled TRLs as described in (A). D. Uptake of 3H-oleate into the indicated tissues after 15 min of administration of 3H-triolein labeled TRLs in the mice from (A). 3H activity in a fixed amount of tissue was normalized to the 1 minute plasma 3H activity for each mouse. Normalized tissue 3H activity is expressed for each tissue relative to the mean of the WT group. E. Hepatic mRNA expression of Lpl and Lipc in mice from (A). Quantitative real-time PCR cycle number for each gene was normalized to that of β-actin. F. Immunoblots of LPL and HL from liver lysates of mice in (A). Immunoblots of the proteins from the lysates for β-actin are shown as a loading control. A, C: *P<0.05, ****P<0.0001, repeated factor 2-way ANOVA. D & E: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, student’s unpaired T-test. Data is expressed as mean ± S.E.M.