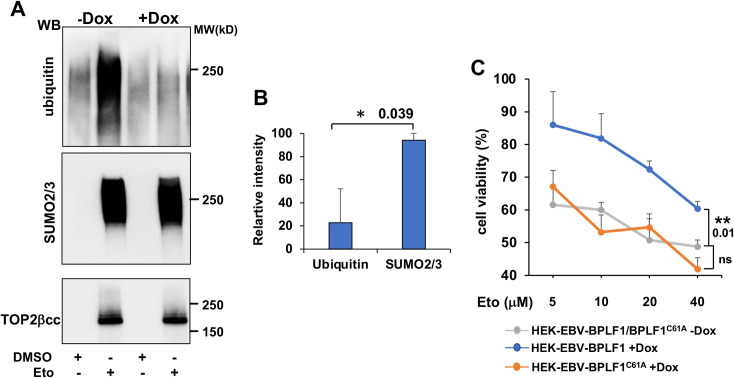
Fig 4. BPLF1 promotes the accumulation of SUMOylated TOP2ccs and cell viability following Etoposide treatment.
(A) HEK-rtTA-BPLF1 cells were cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence of 1.5 μg/ml Dox and then treated with 80 μM Etoposide for 30 min followed by detection of DNA trapped TOP2 by RADAR assay. Western blots of proteins bound to 10 μg DNA were probed with antibodies to TOP2, ubiquitin and SUMO2/3. The expression of BPLF1 was associated with strongly decreased ubiquitination of the TOP2ccs while SUMOylation was only marginally affected. (B) The intensity of the ubiquitin/SUMO2/3 smears and TOP2 specific bands was quantified by densitometry using the ImageJ software. Relative intensity was calculated as intensity of the smears in Dox-treated versus untreated cells after normalization to the total amount of DNA-tapped TOP2. Mean ± SE of two independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test. *P≤0.05. (C) HEK-rtTA-BPLF1/BPLFC61A cells were cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence of 1.5 μg/ml Dox and then treated overnight with the indicated concentration of Etoposide before assessing cell viability by MTT assays. The expression of catalytically active BPLF1 decreased the toxic effect of Etoposide over a wide range of concentrations while BPLF1C61A had no appreciable effect. The mean ± SD of two independent experiments is shown. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test. **P≤0.01; ns = non-significant.