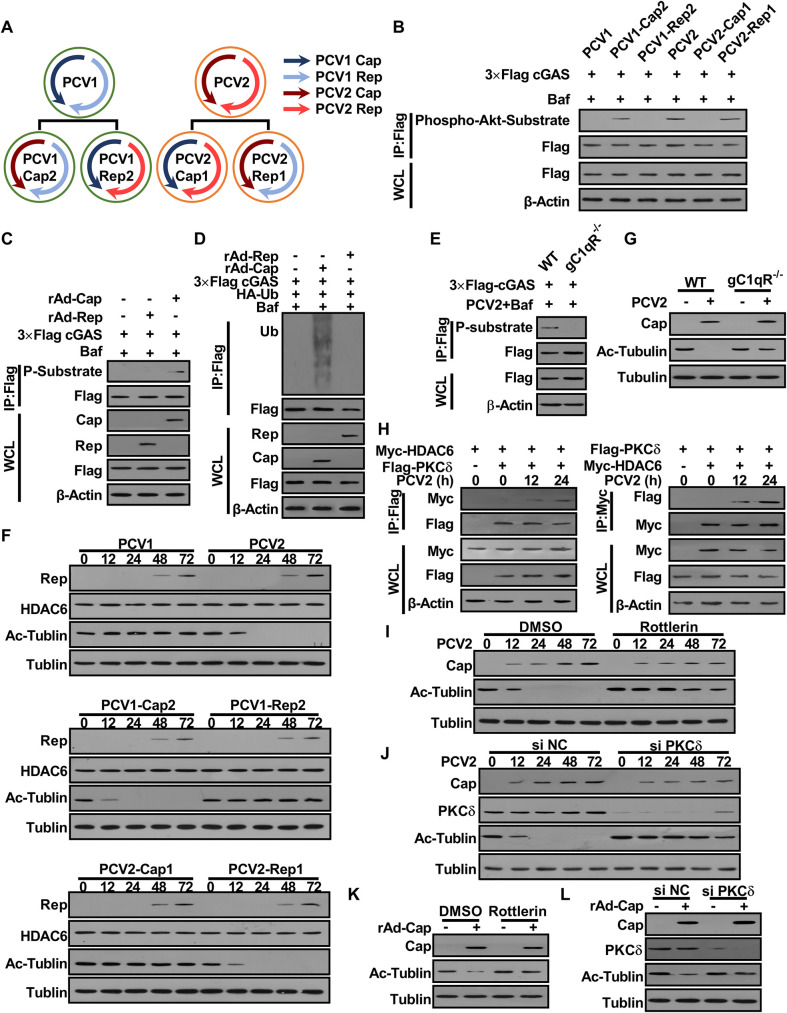
Fig 7. PCV2 Cap plays a predominant role in promoting porcine cGAS phosphorylation and HDAC6 activation depending on gC1qR and/or PKCδ.
(A) Model of construction of PCV mutants. (B-D) Cap is a critical regulator of cGAS phosphorylation. PK-15 cells were infected with PCV mutants (MOI = 5) for 12 h, and then the phosphorylation level of cGAS at the S278 site was detected by western blotting (B). PK-15 cells were infected with rAd-Blank (MOI = 100), rAd-Rep (MOI = 100) and rAd-Cap (MOI = 100) for 24 h, then the phosphorylation (C) and the poly-ubiquitination levels (D) of cGAS were detected by immunoprecipitation. (E) gC1qR-/- PK-15 cells and wild type PK-15 cells were infected with PCV2 (MOI = 5) for 12 h, then the phosphorylation of cGAS was detected by immunoprecipitation. (F) Cap is a critical regulator of HDAC6 activation. PK-15 cells were inoculated with PCV mutants (MOI = 5) for the indicated time, and then the levels of HDAC6 and Ac-tubulin were determined by western blotting. (G) gC1qR-/- PK-15 cells and wild type PK-15 cells were infected with PCV2 (MOI = 5) for 48 h, then the levels of Ac-Tubulin detected by western blotting. (H) Interaction of PKCδ with HDAC6. PK-15 cells were transfected with Myc-HDAC6 and Flag-PKCδ for 24 h. Then these cells were infected with PCV2 (MOI = 5) for indicated time; the interaction of HDAC6 with PKCδ was analyzed. (I) PK-15 cells were pretreated with Rottlerin and infected with PCV2 (MOI = 5) for the indicated time, and then the levels of Ac-Tubulin were determined by western blotting. (J) PK-15 cells were transfected with PKCδ specific siRNA (siPKCδ) or siRNA negative control (siN.C.) for 24 h and then infected with PCV2 (MOI = 5) for the indicated time, followed by western blotting detection of the levels of Ac-Tubulin. (K, L) PK-15 cells were pretreated with Rottlerin (K), or transfected with PKCδ specific siRNA (siPKCδ) or siRNA negative control (siN.C.) (L), and then infected with rAd-Cap (100 MOI) for 24 h, followed by western blotting detection of the levels of Ac-Tubulin.