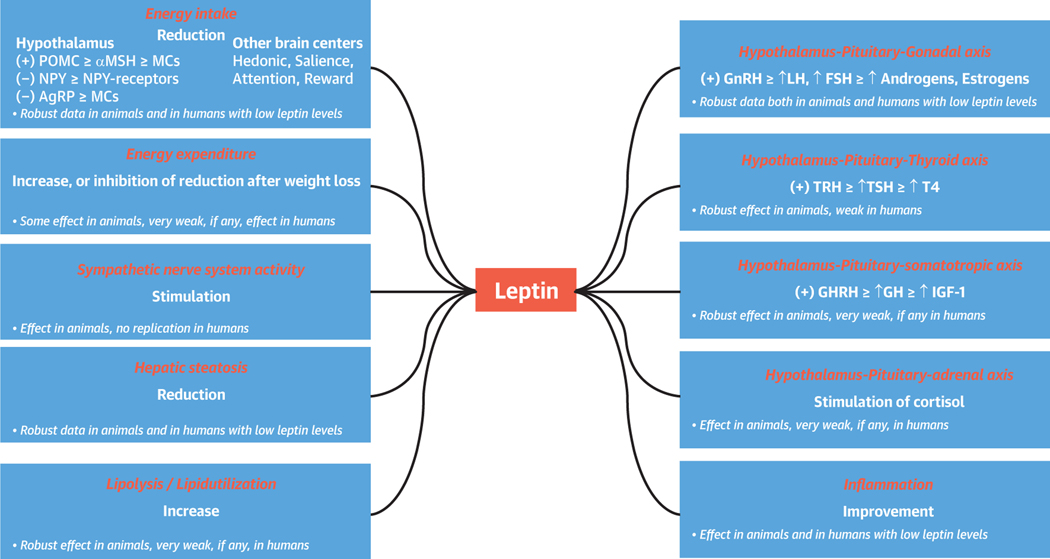
FIGURE 1. Main Effects of Leptin on Metabolism and Endocrine Function in Mouse Models and Humans.
In animals, Leptin has demonstrated robust effects on energy intake and expenditure as well as in sympathetic nervous system activity, Lipid metabolism, inflammation, liver function, and hypothalamic-pituitary function. In humans, leptin treatment is effective mainly in conditions of complete or mild leptin deficiency, in which it decreases energy intake, induces lipid catabolism, improves immune response, and restores the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonadal axis. AgRP = agouti-related peptide; αMSH = α-melanocyte stimulating hormone; FSH = follicle-stimulating hormone; GH = growth hormone; GHRH = growth hormone-releasing hormone; GnRH = gonadotropin-releasing hormone; IGF = insulin-like growth factor; LH = luteinizing hormone; MCs = melanocortins; NPY = neuropeptide Y; POMC = pro-opiomelanocortin; T4 = thyroxine; TRH; TRH = thyrotropin-releasing hormone; TSH = thyroid- stimulating hormone.