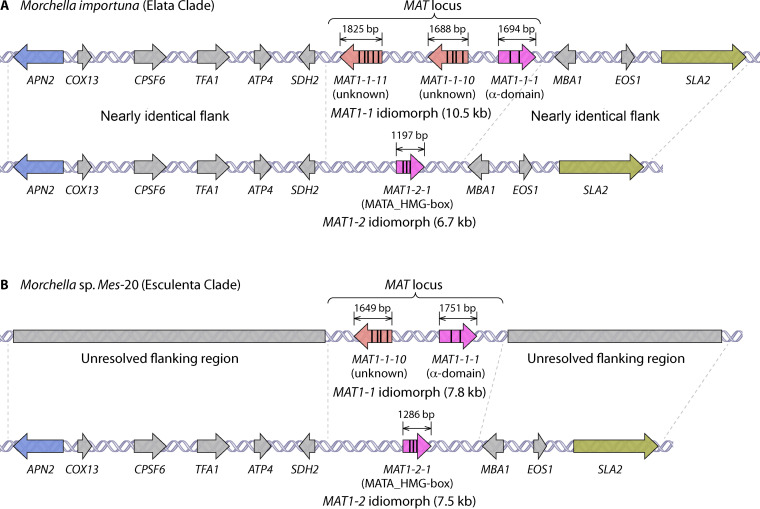
FIG 2.
Structure of the MAT locus of Morchella importuna (Elata clade) (A) and Morchella sp. Mes-20 (Esculenta clade) (B). Introns are represented inside the MAT genes with vertical black lines. At the MAT locus, either a MAT1-1 or MAT1-2 idiomorph is present, containing at least a MAT1-1-1 α-domain gene or a MAT1-2-1 MATA_HMG-box gene, respectively. In addition, further genes are present in the MAT1-1 idiomorph: MAT1-1-10 and MAT1-1-11 in M. importuna (A) and MAT1-1-10 in Morchella sp. Mes-20 (B). The genes flanking the MAT idiomorphs are fairly well conserved. The flanking region of the MAT1-1 idiomorph of Morchella sp. Mes-20 has not yet been revealed. APN2 encodes an abasic endonuclease/DNA lyase; COX13 encodes the cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIa; CPSF6 encodes cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 6; TFA1 encodes transcription initiation factor IIE subunit alpha; ATP4 encodes mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase subunit 4; SDH2 encodes succinate dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) iron-sulfur subunit; MBA1 encodes mitochondrial inner membrane-associated mitoribosome receptor; EOS1 encodes N-glycosylation protein; and SLA2 encodes a protein that binds to cortical patch actin. Distances and sizes are not drawn to scale. Mating-type structures from M. importuna and Morchella sp. Mes-20 were summarized from references 20–24 and our unpublished data.