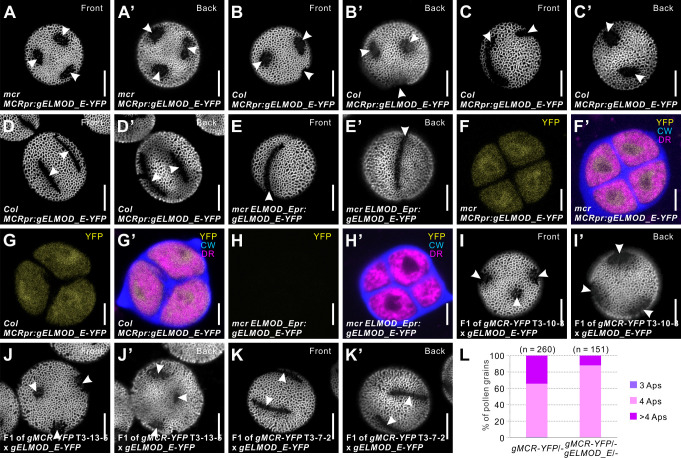
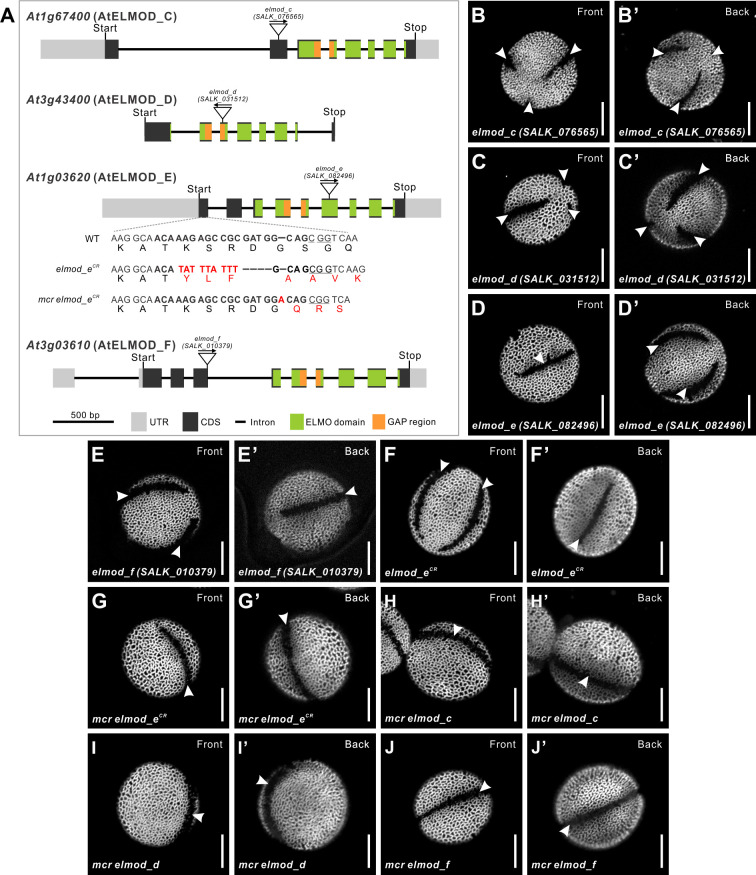
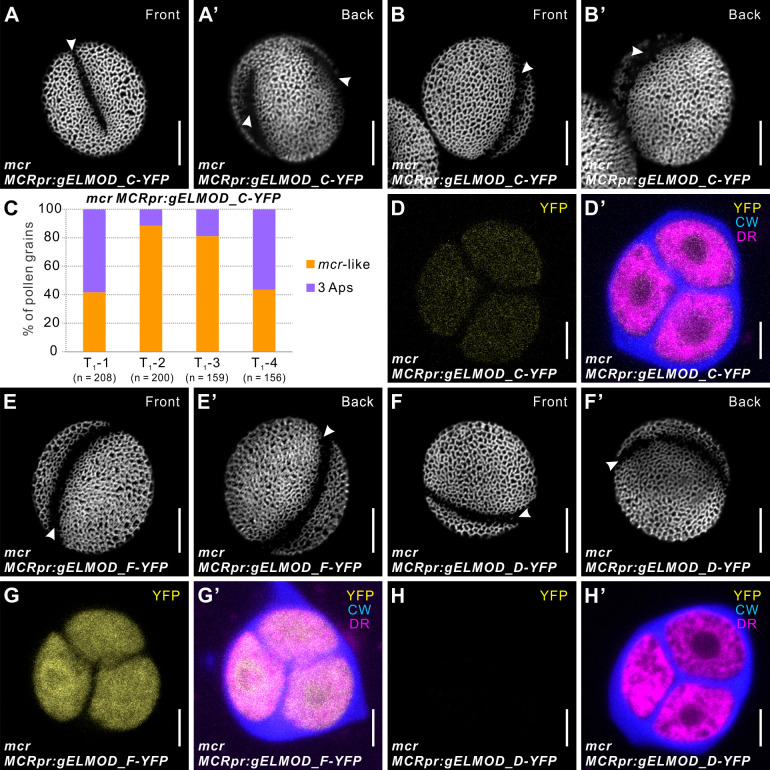
Figure 9. Arabidopsis ELMOD_E can affect aperture patterns.
(A–D’) Pollen grains from mcr (A, A’) and Col-0 (B–D’) plants expressing MCRpr:gELMOD_E-YFP. (E, E’) Pollen grain from mcr plants expressing ELMOD_Epr:gELMOD_E-YFP. (F–H’) Confocal images of tetrads expressing MCRpr:gELMOD_E-YFP and ELMOD_Epr:gELMOD_E-YFP. Adjacent panels show YFP signal (α) and merged signal (α’) from YFP, Calcofluor White (CW), and CellMask Deep Red (DR). (I–K’) Pollen grains from the F1 plants produced by crossing mcr MCRpr:gELMOD_E-YFP with three T3 lines of mcr MCRpr:gMCR-YFP (with single homozygous insertions of the MCR-YFP transgene, expressed, respectively, at low, medium, and high levels). (L) Percentage of pollen grains with indicated number of apertures in the pollen populations from F1 progeny of the mcr MCRpr:gMCR-YFP T3-7-2 line crossed with mcr or with mcr MCRpr:gELMOD_E-YFP. Number of analyzed pollen grains (from at least two individual plants) is indicated. Apertures are indicated with arrowheads. Scale bars, 10 μm for pollen and 5 μm for tetrads.