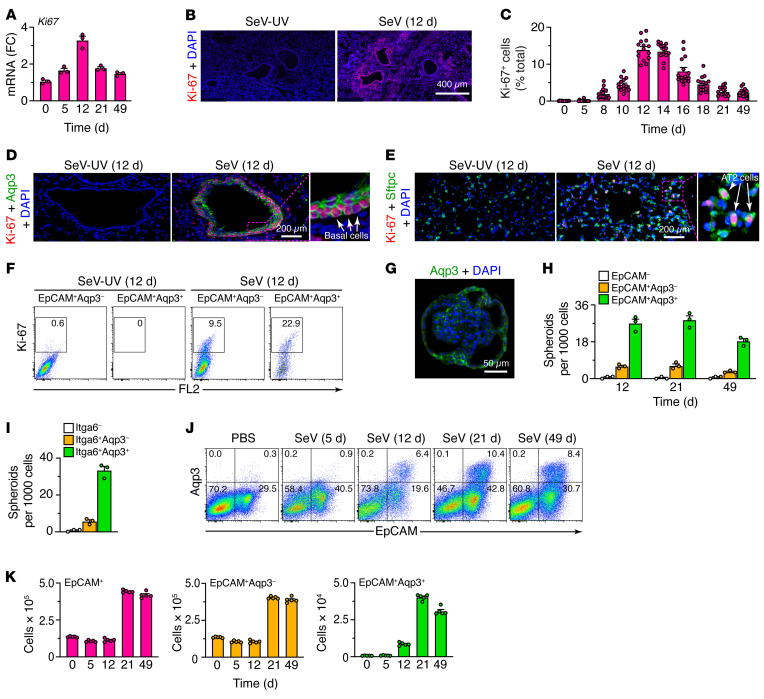
Figure 4. Basal ESC growth after SeV infection.
(A) Levels of Ki67 mRNA in lung tissue from WT mice 0–49 days after SeV infection. (B) Immunostaining for Ki-67 in lung sections 12 days after SeV infection. Scale bar: 400 μm. (C) Quantitation of Ki67+ cells in lung sections 0–49 days after SeV infection. (D) Immunostaining for Ki-67 and Aqp3 in bronchiolar-alveolar sections 12 days after SeV or SeV-UV infection. Scale bar: 200 μm. Original magnification, x3.0 (inset). (E) Immunostaining for Ki-67 and Sftpc in alveolar sections 12 days after SeV or SeV-UV infection. Scale bar: 200 μm. Original magnification, x3.2 (inset). (F) Flow cytograms for Ki-67 in lung epithelial (CD31–CD45–EpCAM+) cells (Aqp3– and Aqp3+ subsets) in WT mice 12 days after SeV or SeV-UV infection. FL2, BluFL2, empty channel. (G) Immunostaining for Aqp3 in a lung spheroid from EpCAM+Aqp3+ cells obtained 21 days after SeV infection and placed into 3D organoid culture. Scale bar: 50 μm. (H) Number of lung spheroids from the indicated cell populations, obtained 12–49 days after SeV infection. (I) Number of lung spheroids from the indicated cell populations, obtained 21 days after SeV infection. (J) Flow cytograms of lung epithelial cells (CD31–CD45– restricted and analyzed for EpCAM and Aqp3) after SeV infection or PBS treatment. Values indicate the percentage of cells within each gate. (K) Numbers of the indicated cell populations using the conditions in J. Data represent results from a single experiment with 3–5 mice per condition, and experiments were replicated twice.