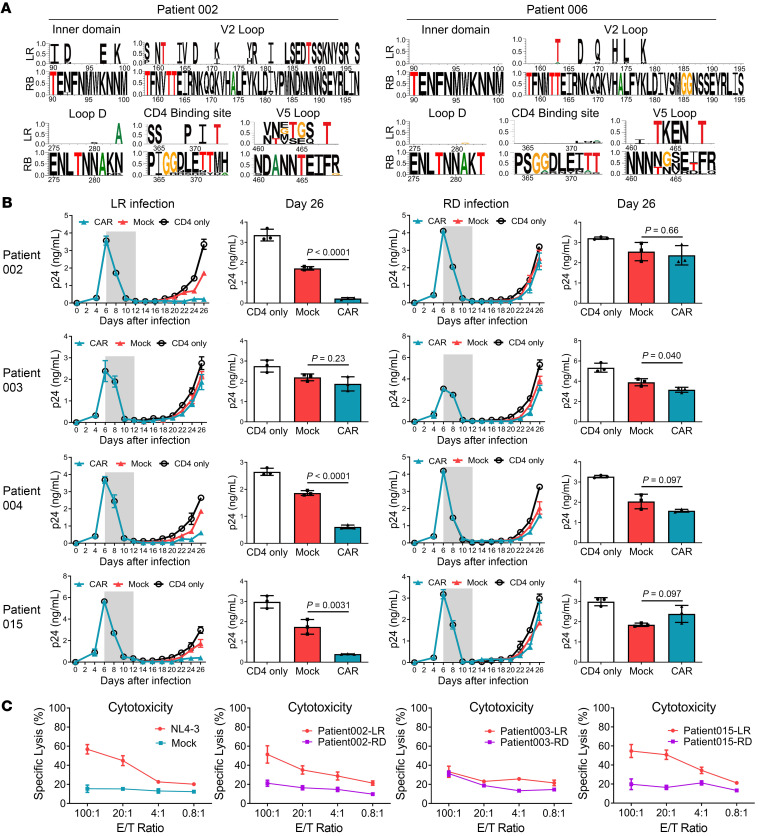
Figure 6. Rebound virus clonality and resistance to bNAb-derived CAR T cell–mediated cytotoxicity.
(A) Clonal Env mutations on inner domain, V2 loop, loop D, CD4-binding site, and V5 loop after viral rebound in patients 002 and 006. All sequences were compared with the consensus of the rebound viruses. The residue numbers are based on HIV-1 HXB2 sequence. The top line shows amino acid differences in the pre–CAR T cell sequences from the rebound consensus. (B) PBMCs were isolated from healthy donors and divided into 2 populations. The CD8+ T lymphocytes were used to generate CAR T cells while the autologous CD4+ T cells were infected with outgrown HIV-1 from pre–CAR T cell latent reservoir (LR) or rebound reservoir (RD) (1 ng/mL p24). Six days after HIV-1 infection, antiretroviral compounds (azidothymidine and lopinavir) were added to the CD4+ T cell culture to inhibit virus production. Then the anti–HIV-1 drugs were withdrawn and CAR or control CD8+ T cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio. Every 2 days the cultures were tested for the presence of p24 in the supernatant, using ELISA. Gray shade represents the addition of antiviral drugs. (C) HIV-1 Env derived from pre–CAR T cell latent reservoir or rebound reservoir was ectopically expressed on the HEK293T cell line. These target cell lines were compared for changes in sensitivity to CAR T cell–mediated specific cytotoxicity. Env derived from HIV-1NL4-3 served as the positive control. Direct killing of target cell lines was tested after 24-hour coculture by detecting LDH release. A 2‑sided P value for the estimated difference in pre–CAR T cell and rebound resistance was calculated. Data represent the mean of triplicate values, and error bars represent SEM. P values were calculated using the 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test with equal variances.