Figure 1.
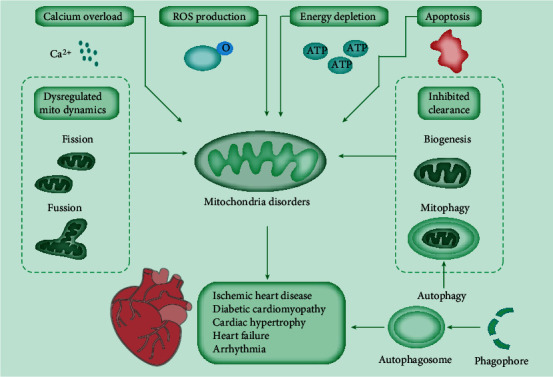
Mitochondrial dysfunctions involved in cardiac disease. Cardiac mitochondria play an important role in energy supply, calcium storage, cell apoptosis, and ROS production. Mitochondrial dynamics through fission and fusion cycles, biogenesis, and mitophagy modulate the mitochondrial pool. Many factors can induce mitochondrial disorders, such as calcium overload, dysregulated mitochondrial dynamics, energy depletion, increased oxidative stress, inhibited damaged mitochondria clearance, and cell apoptosis. Efficient autophagy is essential for the homeostasis of cardiac metabolism. The defects of autophagy or its special type, mitophagy, would ultimately lead to heart-related diseases. The consequences of mitochondrial dysfunction in the heart include ischemia/reperfusion injury, diabetic cardiomyopathy, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
