FIGURE 1.
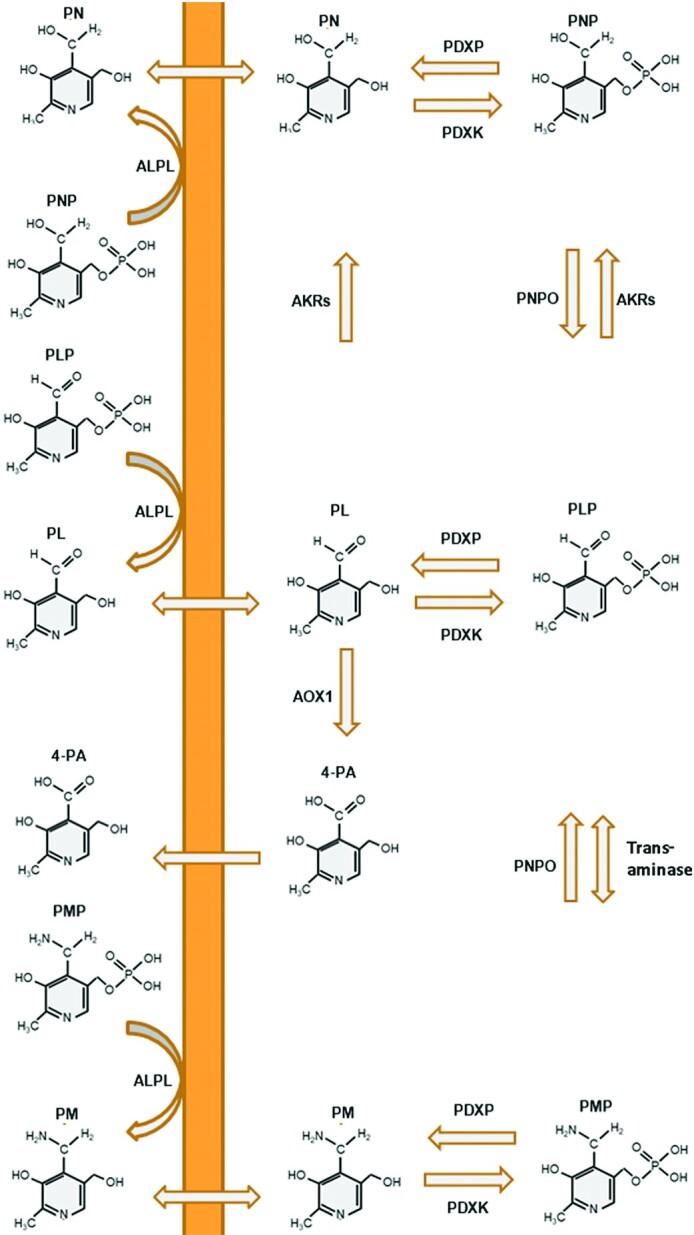
The vitamin B-6 salvage pathway. The different vitamers are converted into PLP through the “B-6 salvage pathway,” involving the enzymes PDXK, PNPO, and PDXP. PLP enters the circulation bound to lysine residues of proteins, mostly albumin. In order to enter the cell, the phosphorylated vitamers are hydrolyzed by ALPL. Once inside the cell, PDXK phosphorylates the different vitamers, yielding PNP, PMP, and PLP. PMP and PNP are converted into PLP by PNPO. Transaminase reactions may also interconvert PMP and PLP as a side reaction. PDXP, along with other phosphatases, hydrolyze phosphorylated vitamin B-6 vitamers, enabling them to exit the cell. PL is eliminated from the body following its conversion to 4-PA, catalyzed by AOX1. AKRs can convert PL and PLP into PN and PNP, respectively; however these activities likely play only a minor role in vitamin B-6 metabolism. AKR, aldo-keto reductase; ALPL, tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase; AOX1, aldehyde oxidase; PDXK, pyridoxal kinase; PDXP, pyridoxal phosphatase; PL, pyridoxal; PLP, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate; PM, pyridoxamine; PMP, pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate; PN, pyridoxine; PNP, pyridoxine-5'-phosphate; PNPO, pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase; 4-PA, 4-pyridoxic acid.
