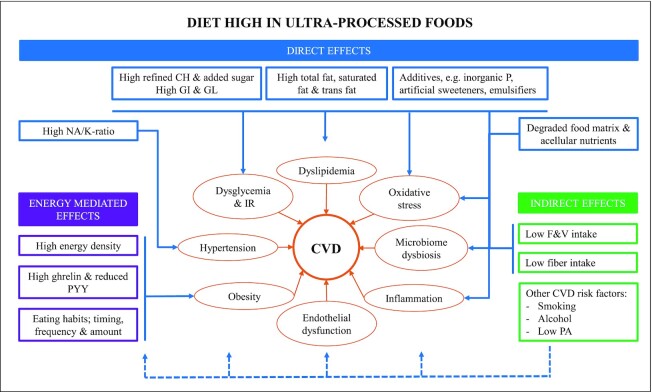
FIGURE 2.
Potential biological mechanisms underlying the association between ultra-processed foods and CVD. The diagram describes plausible biological pathways through which a diet high in ultra-processed foods may contribute to CVD. Key mechanisms include altered serum lipid concentrations, modified gut microbiota and host–microbiota interactions, obesity, inflammation, oxidative stress, dysglycemia, insulin resistance, and hypertension and hormonal imbalances. Arrows indicate stimulation of a pathway. CH, carbohydrates; CVD, cardiovascular disease; F&V, fruit and vegetables; GI, glycemic index; GL, glycemic load; IR, insulin resistance; NA/K-ratio, sodium-to-potassium ratio; P, phosphorus; PA, physical activity; PYY; peptide YY.