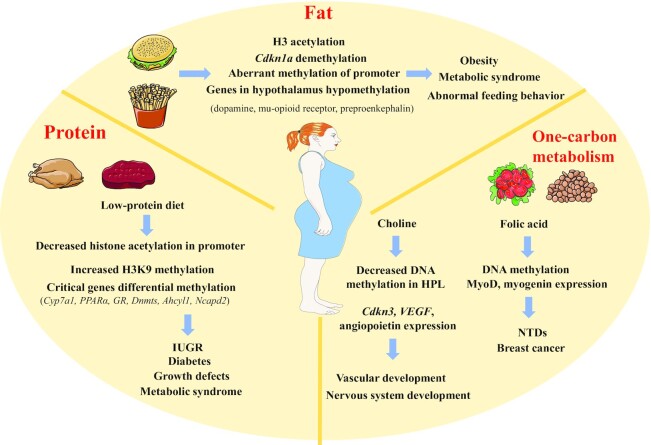
FIGURE 3.
Nutritional regulation of epigenetic modification. During pregnancy, maternal nutrition concentrations greatly influence the health of the fetus through epigenetic regulation. Fat, protein, and one-carbon metabolism can affect the epigenetics of the mother of fetuses in different ways. Ahcyl, adenosylhomocysteinase like 1; Cdkn1a, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; Cyp7a1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; HPL, hippocampal neuroepithelial layer; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction; Ncapd2, non-SMC condensin I complex subunit D2; NTD, neural tube defect; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.