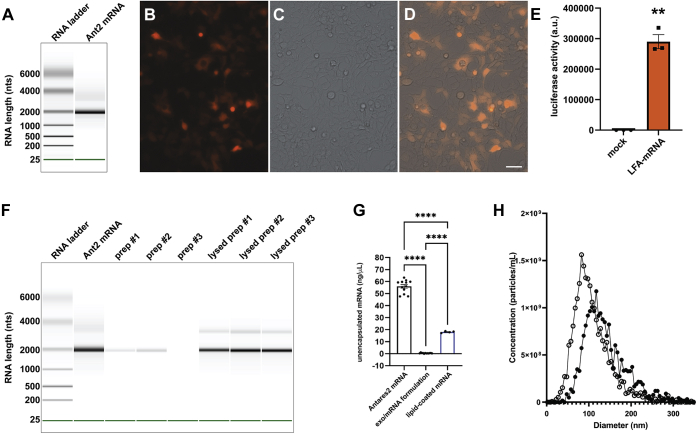
Figure 4.
Characterization of Antares2 mRNA and mRNA-loaded exosomes.A, gel-like image of in vitro synthesized Antares2 mRNA interrogated using an RNA chip on an Agilent Bioanalyzer. B–D, fluorescence and brightfield micrographs of HEK293 cells 2 days after transfection with Antares2 mRNA. Cells were grown on sterile, poly-L-lysine-coated coverglasses, fixed, mounted, and imaged using an EVOS M7000 microscope system. Bar, 50 μm. E, bar graph of luciferase activity of HEK293 cells measured 2 days after transfection with Antares2 mRNA. Cells were grown in 96 well plates, DTZ solution was added, and light emission measured using a plate reader. Bar height represents average light emission, hatched line represents standard error of the mean, and asterisks represent Student's t test, with ∗∗ denoting p < 0.005. F and G, efficient encapsulation of mRNA by lipid-mediated exosome loading. F, gel-like image of RNA markers and samples separated on an RNA chip in an Agilent Bioanalyzer. Data is presented, left to right, for Antares2 mRNA, three separate mRNA-loaded exosome preparations, and the RNA extracted from these same preparations. G, bar graph of Ribogreen fluorescence-based measurement of free accessible RNA concentrations, measured using a plate reader relative to RNA standards of known concentration, for matched samples of Antares2 mRNA, Antares2 mRNA-loaded exosomes, and Antares2 mRNA coated with cationic lipids (n ≥ 6; bar height represents the average, hatched lines represent standard error of the mean, and asterisks denote statistical significance calculated by one-way ANOVA, with ∗∗∗∗ <0.0001). H, size distribution profile of (open circles) purified exosomes and (closed circles) exosomes that had been loaded with Antares2 mRNA, as determined by NTA.