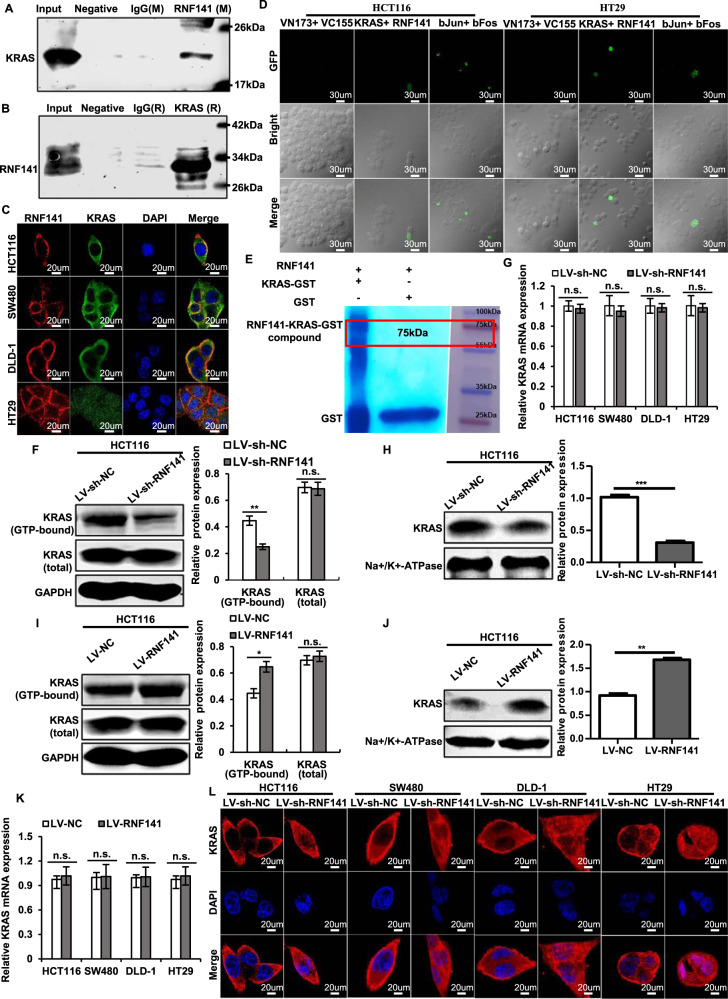
Fig. 6. RNF141 interacts with KRAS and upregulates KRAS activity by promoting its membrane translocation.
A, B Immunoprecipitation (IP) was conducted using RNF141 antibody (mouse derived) and followed by Western blot using KRAS antibody (rabbit derived) (A); meanwhile, IP using KRAS antibody and followed by Western blot using RNF141 antibody (B). IgG antibody (rabbit or mouse derived) was used as non-specific control. C The colocations between RNF141 and KRAS in CRC cells were determined by double immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar, 20 μm. D The direct visualization of RNF141 and KRAS interaction in HCT116 and HT29 cells were demonstrated by BiFC assay. bJunVN173 and bFosVC155 were used as positive control, VN173 and VC155 were used as negative control. E Detection of full-length RNF141 bound to KRAS-GST or GST in a GST pull-down assay. F, I Active KRAS was assessed by K-Ras Activation Assay Kit in HCT116 cell transfected with indicated lentivirus. Meanwhile, whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blot for total KRAS detection. G, K RNF141 mRNA levels were validated in HCT116, SW480, DLD-1, and HT29 cells by real-time PCR. H, J KRAS protein levels of membrane extraction in CRC cells transfected with indicated lentivirus was assessed by Western blot. Na+/K+-ATPase was used as membrane internal control. L The effect of RNF141 knockdown on KRAS membrane/cytoplasmic localization was visualized by IF assay. Scale bar, 20 μm. Bar graphs were presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. n.s. represents no significance.