Figure 1.
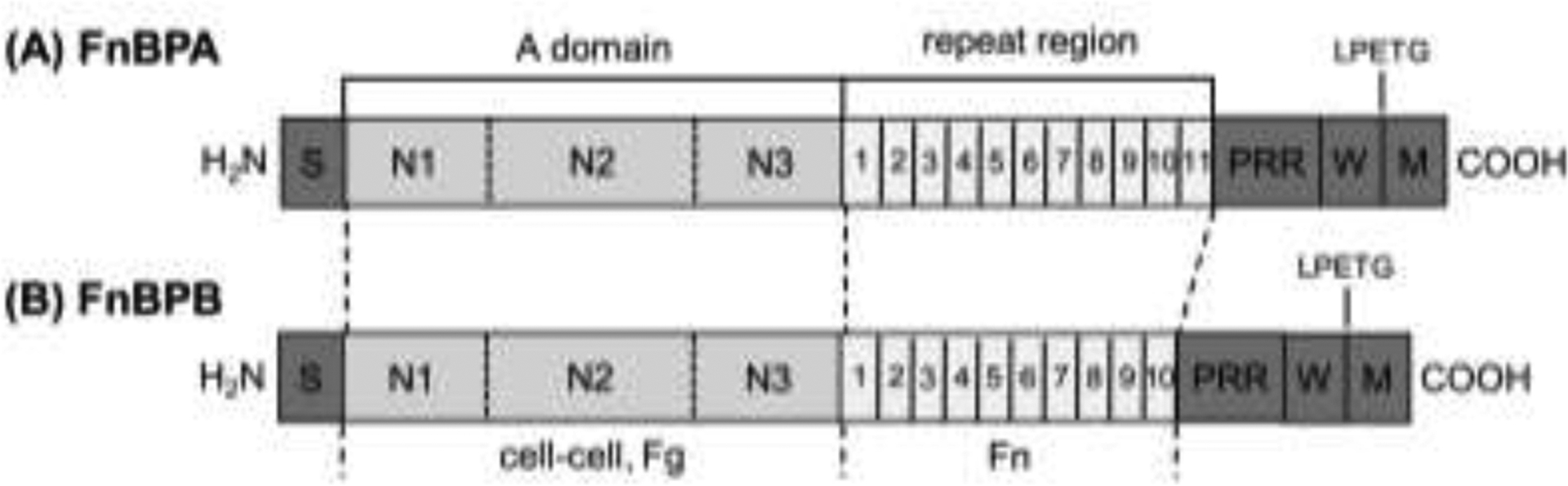
Schematic representation of fibronectin binding protein A (FnBPA) and B (FnBPB) of S. aureus 8325-4. The N-termini of FnBPA and FnBPB contain a signal sequence (S) followed by the A domain that comprises subdomains N1, N2, and N3 that are involved in cell-cell aggregation, and binding to fibrinogen (Fg) and elastin. The A-domain of FnBPB has also been shown to bind fibronectin (Fn). Following the A domains are tandemly repeated fibronectin-binding motifs (numbered). At the C-termini are proline-rich repeats (PRR), wall (W)- and membrane (M)-spanning domains, and the sortase recognition motif LPETG. Identity percentage for the A region between the two proteins is 45%, whereas the repeat region is 94% (Jonsson, et al., 1991).
