Figure 2 |. Multivariate genome-wide association analysis of EXT with Genomic SEM.
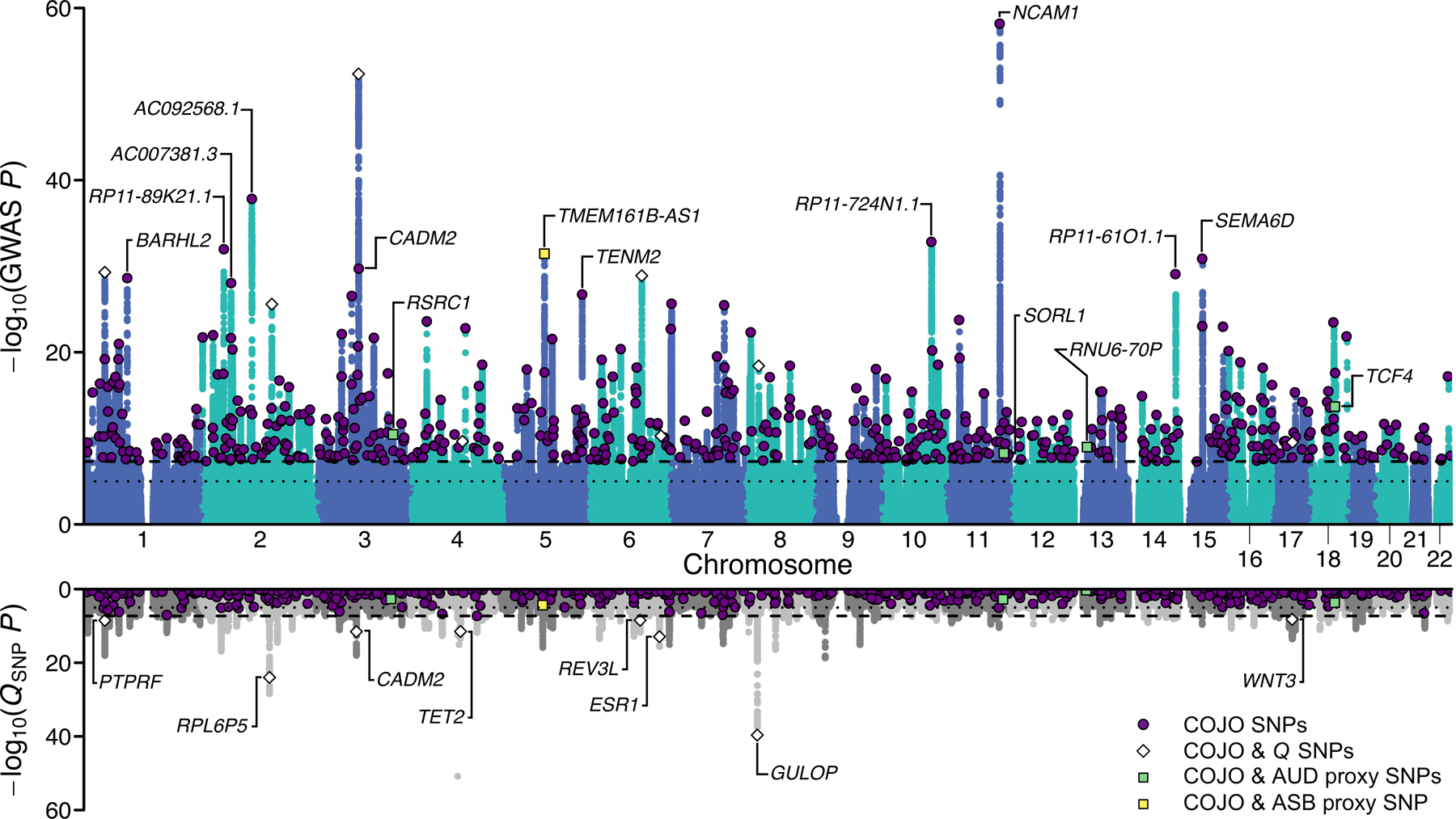
Scatterplot of −log10(P value for two-sided Z-test) for weighted least squares regression to estimate GWAS associations (top panel) and −log10(P value for one-sided χ2 test with 7–1 degrees of freedom) for QSNP tests of heterogeneity (bottom panel) for EXT. Purple dots represent the 579 EXT SNPs that are conditionally and jointly associated (COJO) at genome-wide significance (two-sided P < 5×10−8) (Supplementary Table 9). White diamonds represent eight of the 579 SNPs that also show significant QSNP heterogeneity. Four green and one yellow squares represent five out of the 579 SNPs that also were Bonferroni-significant proxy-phenotype associations with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and antisocial behavior (ASB), respectively (Supplementary Table 11–12). Gene names refer to the closest gene based on genomic location, displayed for a selection of the findings (Supplementary Table 9 reports the nearest gene for all 579 EXT SNPs).
