Fig 4. FDA-approved autophagy activators (FAAs) were ranked based on their therapeutic effects in a zebrafish embryonic AIC (eAIC) model.
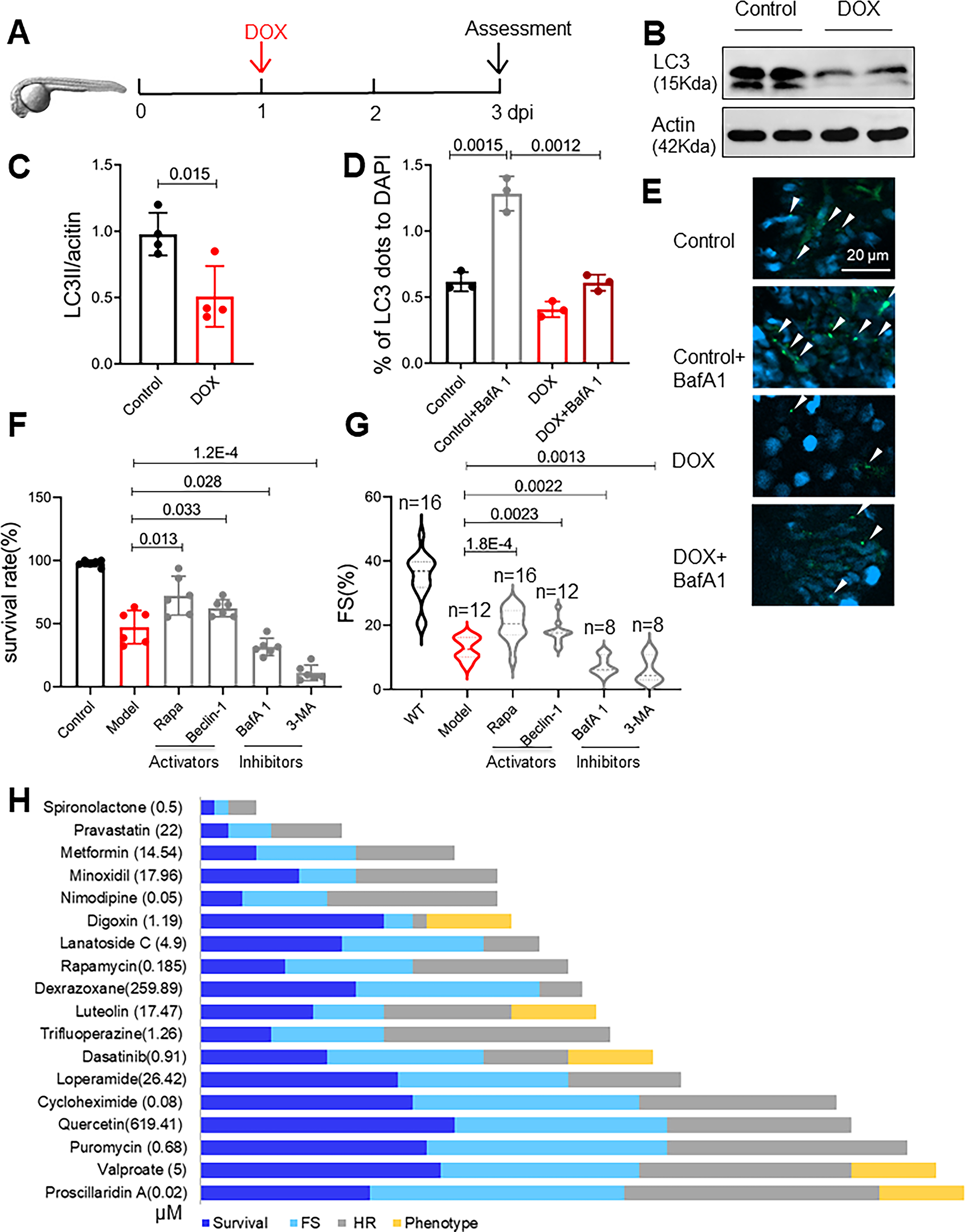
(A) Schematics of the experimental procedure for an embryonic AIC (eAIC) model. (B and C) Representative Western blot of LC3-II in eAIC and LC3-II quantification (n=4/group). (D and E) Tg(GFP-LC3) zebrafish were used to quantify LC3-II induction. Arrows indicate LC3 aggregates. (n=3/group). (F and G) Autophagy activators exert therapeutic effects, and autophagy inhibitors exert detrimental effects on eAIC, as indicated by changes in both mortality and cardiac function. (H) The rank of the top 18 FAA drugs based on a composite score of their therapeutic effects based on survival rate, heart rate, heart function and phenotypes. Mann-Whitney test in (C); Kruskal-Wallis test followed by post hoc Tukey’s test in (D), (F) and (G); Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Bonferroni post hoc test in (G).
