Fig 7. Spironolactone (Spi) and rapamycin (Rapa) activated autophagosome formation in an Atg7-dependent fashion.
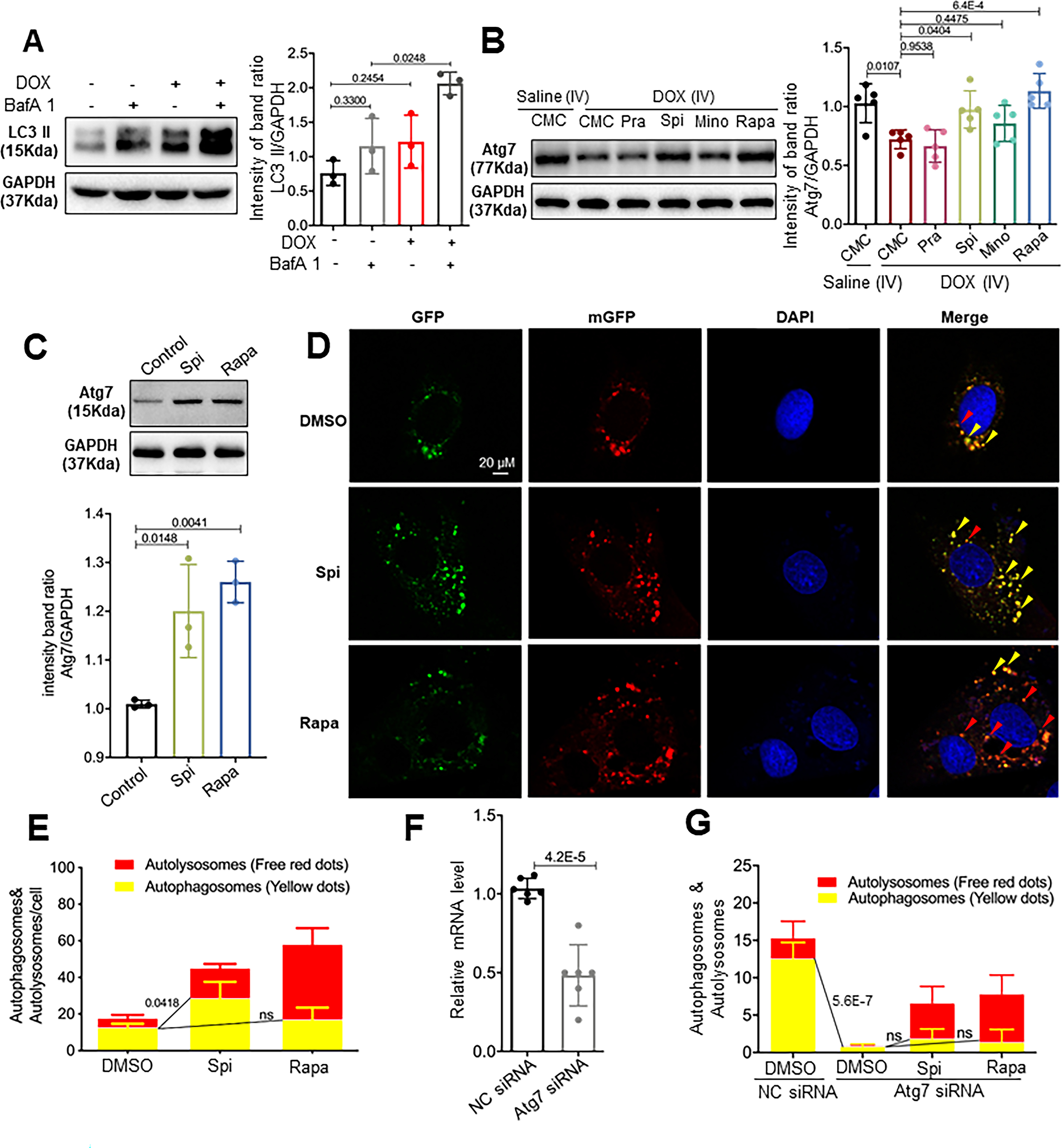
(A) Representative Western blot and quantification of the relative amounts of LC3-II in the hearts from mice injected with a single bolus of DOX. Activated LC3-II and an increased response to BafA1 (n=5/treatment) were observed. (B) Representative Western blots and quantification of Atg7 from the hearts of mice administered the four drugs daily in the later phase. (C) Representative Western blot and quantification of Atg7 from the H9C2 cardiac cell line. Spi and Rapa induced an increase in Atg7 protein levels. (D) H9C2 cells were transiently transfected with mRFP-GFP-LC3 adenovirus and then treated with Spi and Rapa. Representative images of GFP-LC3 and mRFP-LC3 puncta are shown. (E) Quantification of the yellow puncta (autophagosomes) and red puncta (autolysosomes) is shown in (D). (F) qRT-PCR was used to confirm that Atg7 transcripts were reduced by Atg7 siRNA. (G) Quantitative analysis of the yellow puncta (autophagosomes) and red puncta (autolysosomes) showing that Atg7 siRNA ablates the induction of autophagosomes induced by Spi or Rapa. Kruskal-Wallis test was used followed by post hoc Tukey’s test in (A) and (C); one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test in (B), (E) and (G); student’s test in (F).
