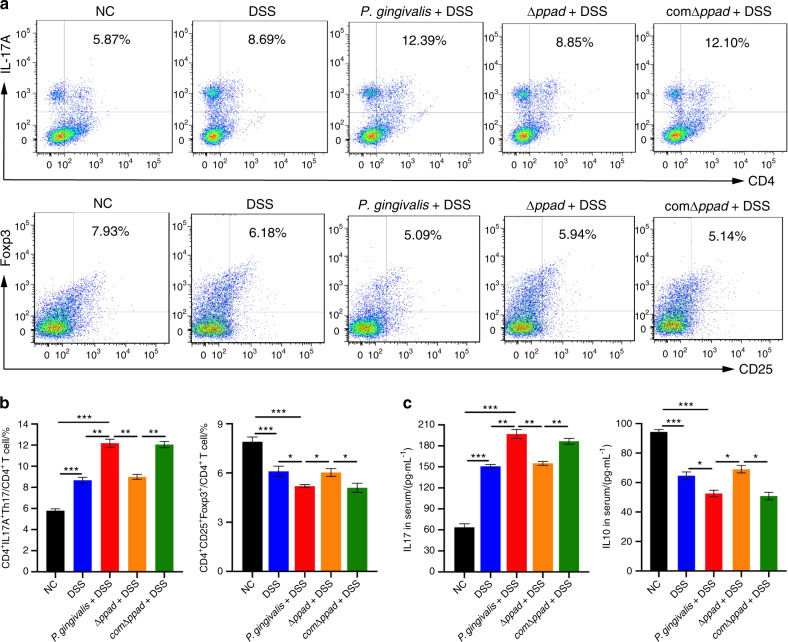
Fig. 5.
P. gingivalis- and comΔppad-exacerbated UC is associated with an imbalance in Th17/Tregs. a, b Flow cytometric analysis and bar chart showing that compared with Δppad, P. gingivalis and comΔppad induced the transformation of CD4+ T cells into proinflammatory Th17 cells and simultaneously inhibited the generation of Tregs (P < 0.05), but no difference was observed between mice administered Δppad and DSS and mice with colitis administered physiological saline (P > 0.05). c ELISA showing that compared with Δppad, P. gingivalis and comΔppad administration caused the increased expression of IL-17 and decreased expression of IL-10 in serum (P < 0.05). The expression levels of the two cytokines were similar in the mice administered Δppad and DSS mice and the mice with colitis (P > 0.05). All indicators were measured with six replicates. The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.000 1 by independent 2-tailed Student’s t test and one-way ANOVA combined with Mann-Whitney U test