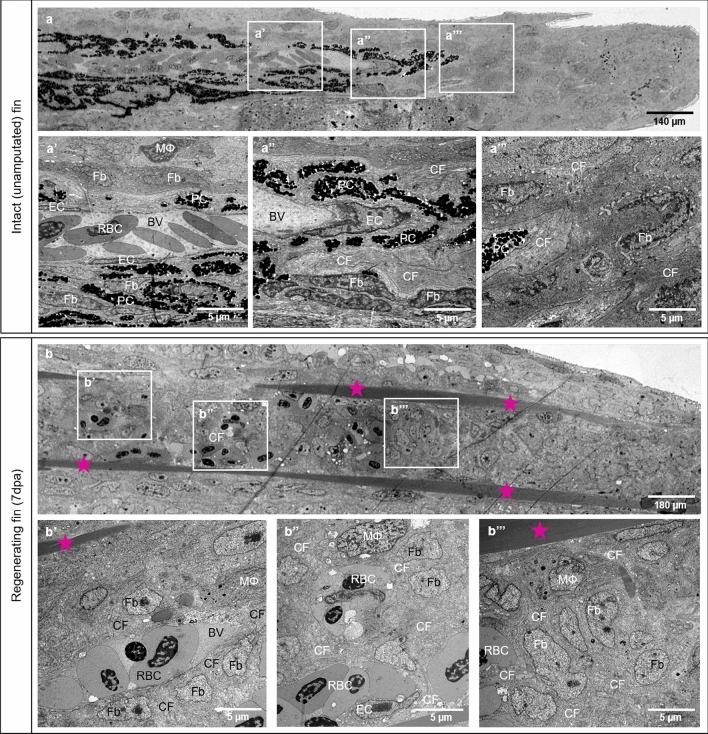
Figure 2.
Differences in tissue compartments between the intact (unamputated) caudal fin and fin during early regeneration. Structural differences between intact caudal fin (a) and early regeneration at 7dpa (b) are demonstrated by transmission electron microscopy. a-a’’ display perfused and mature blood vessel with quiescent and well-differentiated endothelial cells (ECs), pigment cells (PC) and ECM containing robust collagen fibers (CF), fibroblasts (Fb) and very seldom solitary macrophage (MΦ). In the regenerating fin (7dpa), robust collagen fibers (CF) are arranged into two densely packed stripes tracing the future ray bones (b, asterisk). Between the latter, new formed, immature blood vessel (BV) containing red blood cells (RBC) are enclosed by scaffold of CF tracing the direction of blood vessel expansion (b’). The CFs are surrounded tightly by Fb and MΦ (b’). At the vascular front, next to new formed capillaries containing ECs, clusters or single RBC are detectible (b’’). In the blastema, multiple Fb proliferate displaying classical mitotic figures; ECM contains CF and MΦ (b’’’). PC are absent during the regenerative phase. Left side - zebrafish trunk, right side - zebrafish tail, images acquired by electron microscope.