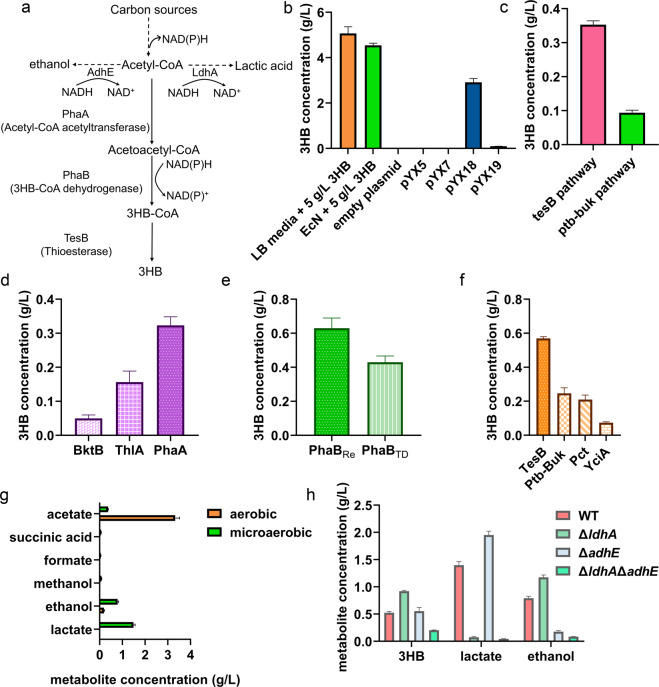
Fig. 1.
Metabolic engineering of E. coli Nissle 1917 for 3HB overproduction. a Biosynthesis pathway for 3HB production utilizing glucose and acetyl-CoA as the substrate. Three enzymes, e.g., acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, 3HB-CoA dehydrogenase, and thioesterase, were employed. Two intrinsic branch pathways are also indicated in the illustration. b Determination of the EcN characteristics for 3HB degradation and biosynthesis. LB media + 5 g/L 3HB was germfree medium supplemented with 5 g/L 3HB. The blank plasmid group was the EcN strain transformed with the pNZ8148 plasmid. The pYX5, pYX7, pYX18, and pYX19 groups consisted of EcN strains transformed with the appropriate plasmids. The Y-axis shows the residual 3HB concentration in media after fermentation. c The 3HB production under microaerobic conditions via different pathways. The groups with EcN overexpressing pathways introduced with corresponding plasmids. d The 3HB yields from various acetyl-CoA acetyltransferases. e The 3HB yields from various 3HB-CoA dehydrogenases. PhaBCn, PhaB from Cupriavidus necator H16; PhaBTD, PhaB from Halomonas bluephagenesis TD01. f The 3HB yields from various thioesterases. g Byproduct concentrations in 3HB fermentation processes under aerobic or microaerobic environments. The pYX50 plasmid was introduced for 3HB production. The monitored metabolites are listed on the Y-axis. h The 3HB, ethanol and lactate production levels under different EcN chassis. The pYX50 plasmid was transformed for 3HB production. Bacteria were grown in LB medium supplemented with 10 g/L glucose. All aerobic fermentation data were acquired after 48 h of cultivation at 200 rpm at 37 °C. Microaerobic fermentation results were obtained at 37 °C without shaking. All data are the mean value of 3 biologically independent experiments, and error bars represent standard deviations