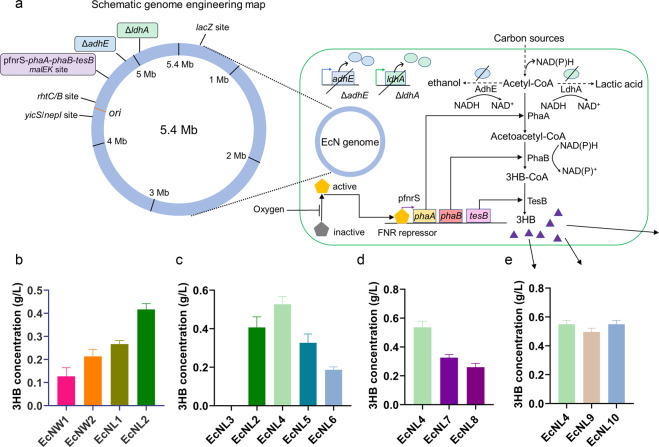
Fig. 2.
Genomic engineering to enhance 3HB production. a Schematic illustration of genome engineering in the EcN strains. The 3HB biosynthesis pathway is shown in the figure. The adhE or ldhA gene was knocked out. The 3HB biosynthesis route was integrated into different genomic sites. The 3HB molecules are presented as purple triangles. b Production of 3HB via different genome insertion strategies. EcNW strains were wild-type EcN integrated with the 3HB pathway. EcNL strains had EcNΔldhA inserted with the pathway. Group 1 had PhaBTD in the biosynthesis route. Group 2 had PhaBCn in the biosynthesis route. c The 3HB yields increased via promoter optimizations. EcNL3 was integrated with a promoterless 3HB biosynthesis pathway. EcNL4, EcNL5, and EcNL6 were inserted with the pathway driven by the pfnrS, J23119, and J23110 promoters. d The production of 3HB with different genomic integration sites. The biosynthesis route was integrated into the malEK, rhtCB and yicS/nepI sites for the EcNL4, EcNL7, and EcNL8 strains, respectively. e Determination of the 3HB yields in the EcN strains containing inserted selection markers. EcNL9 and EcNL10 were EcNL4 strains integrated with the ampR gene and sfGFP gene. Cells were grown in LB medium with 10 g/L glucose. Microaerobic fermentation results were acquired at 37 °C without shaking. All data represent the mean of 3 biologically independent parallel samples, and error bars indicate standard deviations