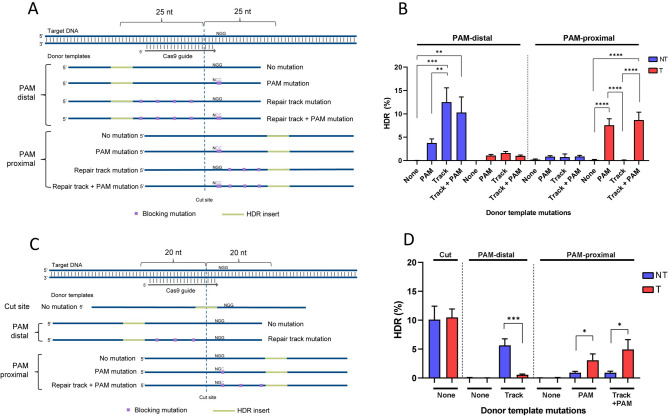
Figure 4.
HDR mutation location determines donor strand preference. (A) Schematic representation of donor templates used to generate PAM-proximal and PAM-distal insertions 25 bases from a Cas9 cut site with no further mutations (None), PAM mutations (PAM), or mutations in the repair track with or without an additional PAM mutation. The NT strand ssODNs are shown. (B) Donor templates creating an EcoRI insertion 25 bases from the cut site at three genomic loci were delivered to Hela cells as the T or NT strand. Donor templates contained no further mutation (None), PAM mutation (PAM), or mutations in the repair track (Track). RNP complexes (Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease complexed with Alt-R CRISPR–Cas9 sgRNA) were delivered at 2 µM along with 2 µM Alt-R Cas9 Electroporation Enhancer and 0.5 µM donor template by nucleofection. Perfect HDR rates were determined by NGS. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of the three sites tested. (C) Schematic representation of donor templates used to generate PAM-proximal and PAM-distal insertions 20 bases from a Cas9 cut site with no further mutations (None), PAM mutations (PAM), or mutations in the repair track with or without additional PAM mutation. The NT strand ssODNs are shown. (D) Donor templates creating an EcoRI insertion at the cut site or 20 bases PAM-proximal or PAM-distal to the Cas9 cut site for 12 genomic loci were tested in Jurkat cells as the T or NT strand. RNP complexes (Alt-R S.p. Cas9 Nuclease complexed with Alt-R CRISPR–Cas9 sgRNA) were delivered at 4 µM along with 4 µM Alt-R Cas9 Electroporation Enhancer and 3 µM donor template by nucleofection. Perfect HDR rates were determined by NGS. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of the 12 sites tested.