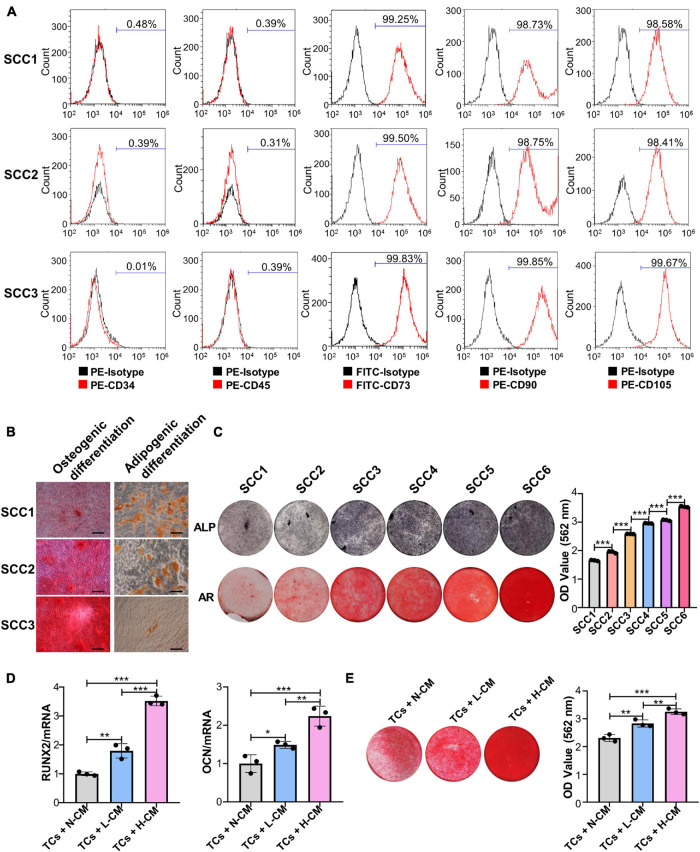
FIGURE 1.
Single-cell colonies with high osteogenic ability had a greater mineralization promotion ability than L-SCCs. (A) The presence of cell surface markers of three SCCs was detected by flow cytometry. (B) The osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation potential of the three SCCs were assessed by Alizarin red and Oil Red O staining. (C) The osteogenic differentiation abilities of SCCs were tested by alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and Alizarin red staining. Alizarin red staining was quantified after the addition of 10% cetylpyridinium chloride. (D) Conditioned medium collected from H-SCCs or L-SCCs was mixed with equal volumes of twofold concentrated osteogenic induction medium, and was used to stimulate the TCs toward osteogenic differentiation for 7 days, following which, the levels of the osteogenic differentiation-related genes in the TCs were tested by RT-qPCR (n = 3). (E) Conditioned medium collected from H-SCCs or L-SCCs was mixed with equal volumes of twofold concentrated osteogenic induction medium, and was used to stimulate the TCs toward osteogenic differentiation for 28 days, following which, the TCs were subjected to Alizarin red staining (n = 3). CM, conditioned medium; TCs, target cells; AR, Alizarin red; N-CM, normal culture medium; L-CM, conditioned medium from L-SCCs; H-CM, conditioned medium from H-SCCs. Scale bar, 50 μm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.