Figure 3.
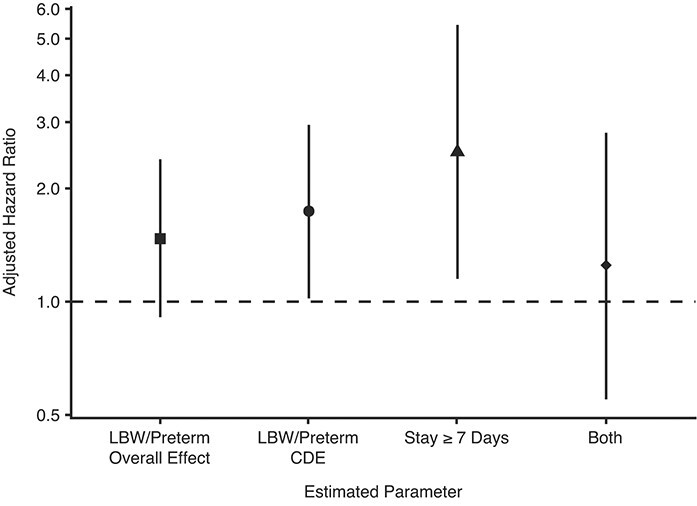
Forest plot visualizing estimates from the piecewise logistic regression model we used to analyze 5,655 observations contributed by 2,115 infants from the Fragile Families and Child Wellbeing Study, a cohort of infants born in large US cities between 1998 and 2000 that oversampled unmarried mothers by design. Eviction, the outcome, is rare, thus, odds ratios approximate hazard ratios. The vertical position of each shape relative to the y-axis represents the magnitude of the estimated association, with ratios relative to uncomplicated births. Vertical black lines represent 95% confidence intervals. “LBW/Preterm Overall Effect” represents our estimate on low birthweight (LBW)/preterm status from model 2 (i.e., not incorporating extended hospital stays). All other bars represent estimates from model 3: the controlled direct effect (CDE) of LBW/preterm birth on eviction, the direct path from an extended hospital stay to eviction (≥7 days in hospital), and the hazard ratio associated with being born LBW/preterm and having an extended hospital stay (reported as “Both”).
