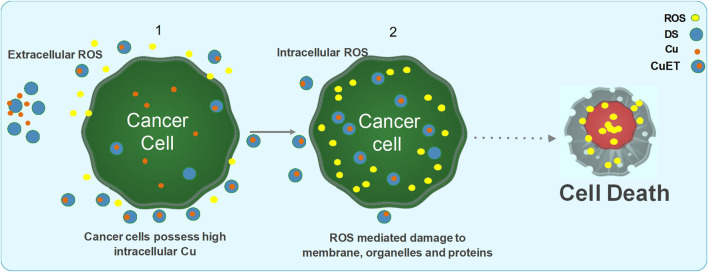
FIGURE 3.
Mechanism of action of DSF/Cu induced anticancer activity. DSF and Cu reaction generates extracellular ROS and damage the membrane proteins. The formation of CuET complex outside the cell and transportation of CuET through lipid bilayer, in addition to increased influx of Cu via the CTR1 transporter, further triggers the intracellular ROS mediated mitochondrial damage and DNA damage leading to apoptosis via the MAPK pathway and JNK activation. CuET also inhibits the proteasome activity via the NPL4/p97 segregase pathway leading to inhibition of NFkB pathway. DSF and CuET further inhibits ALDH mediated ROS detoxification and Pgp mediated drug efflux mechanisms. Collectively, all the above negatively effects the cancer cell survival and maintenance of stemness and resistance thereby sensitizing the cells to ROS and anticancer drug mediated damage, eventually leading to apoptosis.