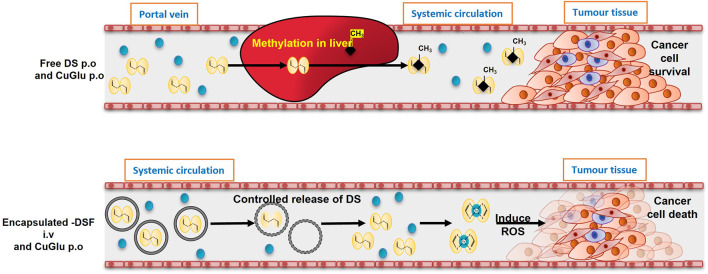
FIGURE 4.
The models of oral and intravenous administration of DS. A. After oral administration, DS will be delivered via portal vein and enriched in liver in which it is instantly methylated. The methylated DS inhibits ALDH and remains its antialcoholism function. Because the thiol group is blocked, its anticancer activity is completely abolished. B. In the new intravenous formulation of DS, the thiol groups in DS are protected. After delivered to cancer tissues, DS chelates copper to generate ROS inducing apoptosis. The end product, DDC-Cu, can penetrate into cancer cells and trigger apoptosis, as well (Tawari et al. Toxicol Res 2015; 4:1439). This hypothesis explained the discrepancy of anticancer activity of DS in the lab and in clinic and the need to develop intravenously applicable nano-encapsulated DS, e.g. liposome and PLGA encapsulated DS.