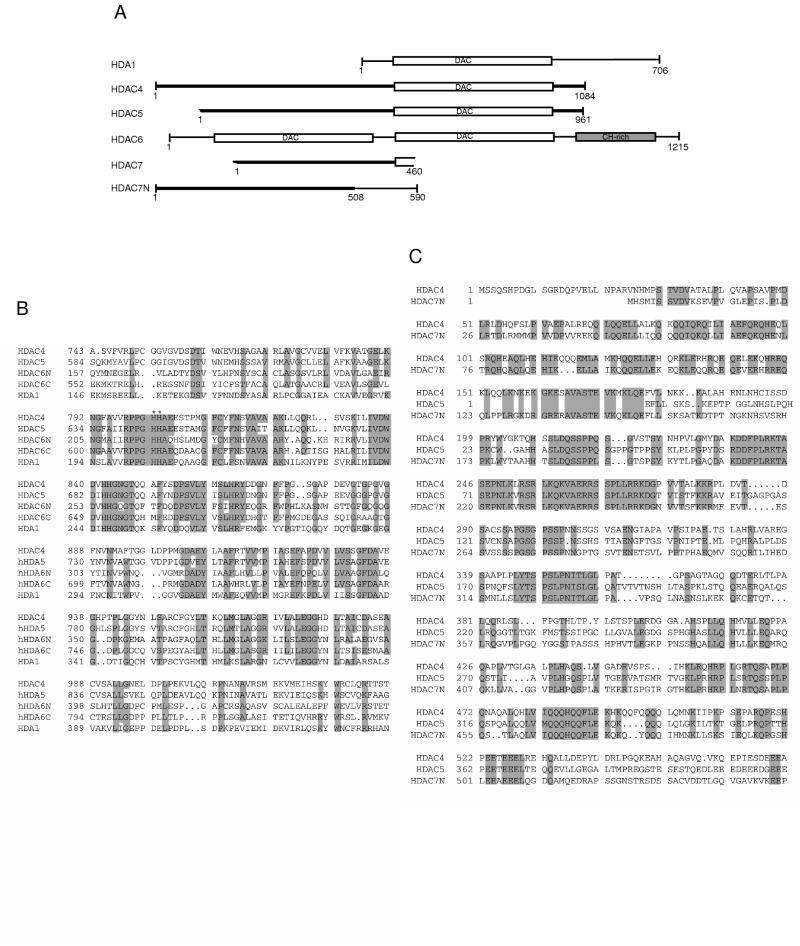
FIG. 1.
Comparison of HDAC4-7 with HDA1. (A) Schematic representation of HDA1 and HDAC4 to -7. The N terminus of HDAC5 is incomplete, as are both termini of HDAC7. HDAC7N may be an alternatively spliced variant of HDAC7. The conserved deacetylase domains are boxed and labeled “DAC.” Other domains shared by HDAC4, -5, and -7 and HDAC7N are shown in bold lines. HDAC6 has a cysteine/histidine-rich domain (CH-rich; shaded box) at its C terminus. This diagram was generated based on BLAST search results. Sequences (GenBank accession numbers) referred to are HDA1 (P53973), HDAC4 (AB006626), HDAC5 (AB011172 and AF039691), HDAC6 (AJ011972), HDAC7 (AF124924), and HDAC7N (AB018287). A genomic clone (GenBank accession no. AC004466) contains some coding sequences related to HDAC4, -5, and -7 and may encode HDAC8. (B) Sequence alignment of catalytic domains of HDAC4 to -6 and HDA1. Identical or highly conserved residues (four of five sequences) are shaded. For simplicity, only S/T, R/K, and D/E are considered to be highly conserved. Asterisks denote histidines 802 and 803 of HDAC4, residues that may be important for deacetylase activity. (C) Sequence alignment of the N-terminal domains of HDAC4, -5, and -7N. Identical residues are shaded.