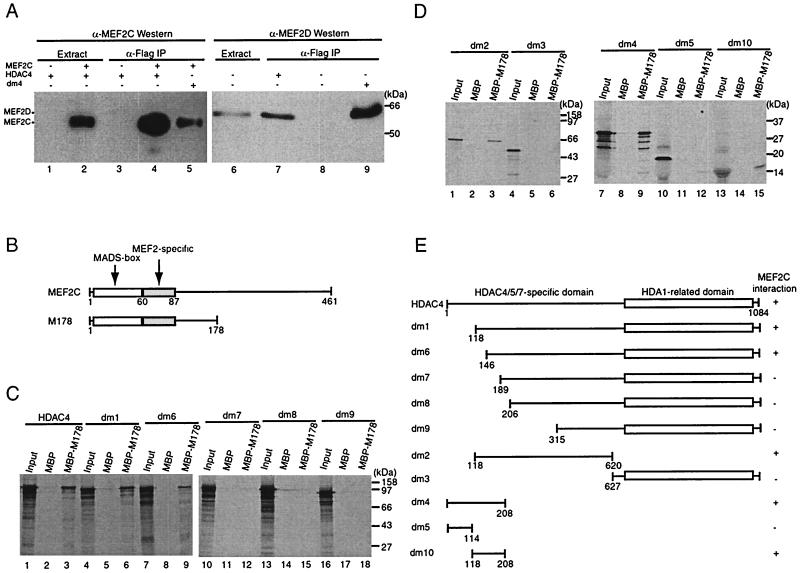
FIG. 6.
HDAC4 interacts with MEF2 in vivo and in vitro. (A) Immunoprecipitation of HDAC4 with MEF2C (lanes 1 to 5) or MEF2D (lanes 6 to 9). Flag-tagged HDAC4 (lanes 1 to 4 and 7) or dm4 (lanes 5 and 9) was expressed with (lanes 2, 4, and 5) or without (lanes 1, 3, and 6 to 9) MEF2C in 293T cells and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Flag M2-agarose. Extracts (lanes 1, 2, and 6) and immunoprecipitated proteins eluted with Flag peptide (lanes 3 to 5 and 7 to 9) were subjected to Western blotting analyses with an anti-MEF2C (lanes 1 to 5) or anti-MEF2D (lanes 6 to 9) polyclonal antibody. The presence of Flag-tagged HDAC4 and dm4 was confirmed by Western blotting analyses of the same samples with an anti-Flag monoclonal antibody (data not shown). (B) Schematic representation of MEF2C and its mutant M178 (consisting residues 1 to 178). (C and D) Interaction of M178 with HDAC4 and its deletion mutants in vitro. MBP or MBP-M178 was immobilized on amylose-agarose and tested for interaction with HDAC4 or its deletion mutants, synthesized in vitro in the presence of [35S]methionine. Input lanes represent 20% of HDAC4 or its mutants used for interaction. (E) Schematic representation of HDAC4 and its deletion mutants used in the interaction assays (A, C, and D). The + symbol denotes that the protein shown at left interacts with MEF2C.