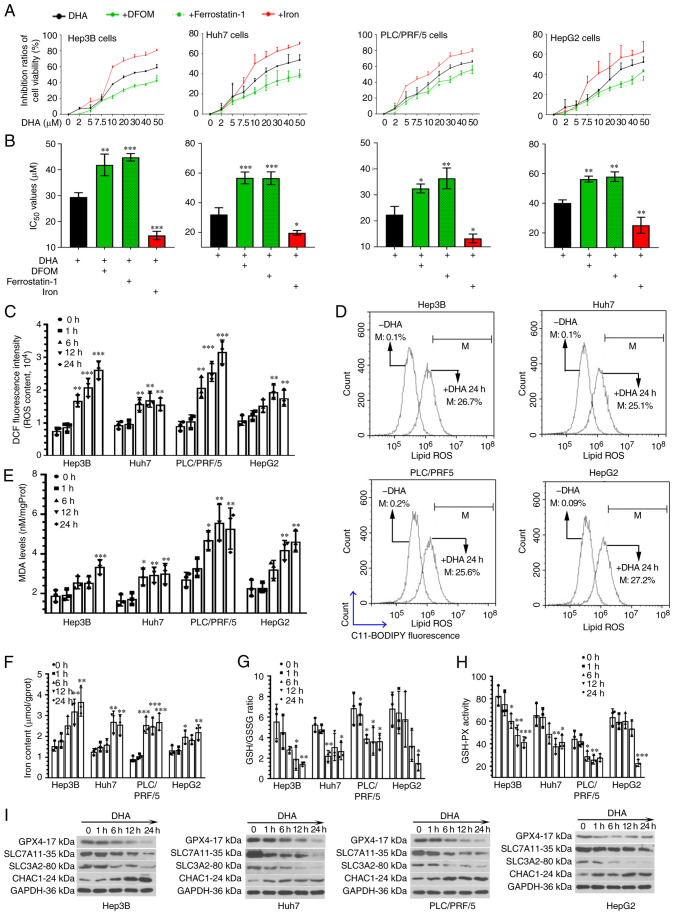
Figure 1.
DHA induces ferroptosis in PLC cells in vitro. (A) Hep3B (p53 null), Huh7 and PLC/PRF/5 (both p53 mutant) and HepG2 (p53 wild-type) cells were treated with increasing concentrations of DHA for 24 h. Two different ferroptosis inhibitors, DFOM (an iron chelator; 10 µM for Huh7 cells and 50 µM for the other cell lines) and ferrostatin-1 (a lipid peroxidation inhibitor; 5 µM for HepG2 and 1 µM for the other cell lines) were used to treat PLC cells in the presence of DHA. Iron chloride hexahydrate (10 µg/ml) was used to increase the iron concentration. The vitality of PLC cells were determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 assays. (B) IC50 values were calculated. (C) Based on the IC50 values, HepG2, Huh7, Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5 were treated with 40, 35, 30 and 25 µM DHA, respectively. After incubation with DHA for 1, 6, 12 or 24 h, (C) total ROS, (D) lipid ROS generation. (E) MDA levels, (F) iron concentrations, (G) GSH/GSSG ratios (H) and GSH-PX activity, as well as (I) the protein expression levels of GPX4, SLC7A11, SLC3A2 and CHAC1 in PLC cells were determined. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three repeats. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs. control (0 h). DHA, dihydroartemisinin; PLC, primary liver cancer; DFOM, deferoxamine mesylate salt; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MDA, malondialdehyde; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; GSH-PX, glutathione-peroxidase; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; SLC, solute carrier family; CHAC, ChaC glutathione specific γ-glutamylcyclotransferase; DCF, dichlorofluorescin; M, % of control.