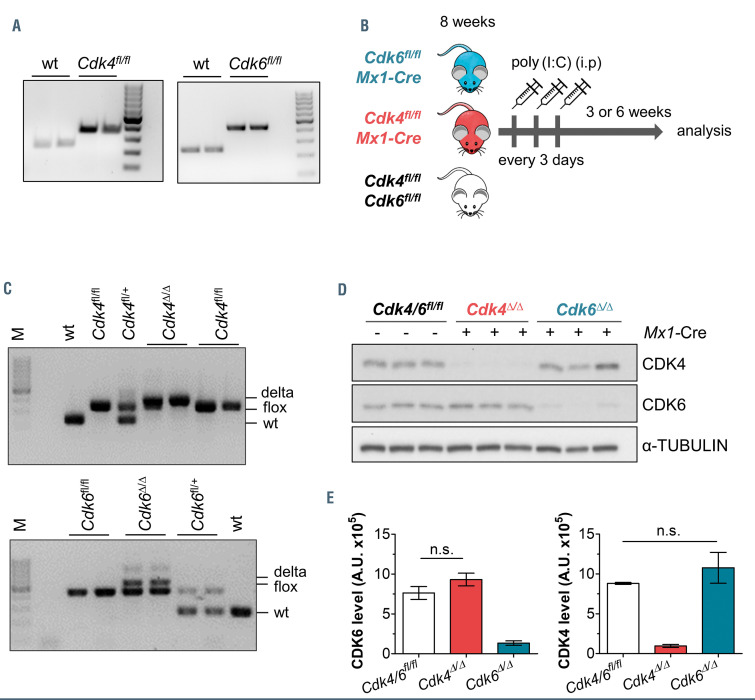
Figure 1.
Reduced CDK4 or CDK6 expression in Cdk4fl/fl or Cdk6fl/fl Mx1-Cre mice. (A) The presence of loxP-flanked Cdk4 (left) or Cdk6 (right) were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on genomic DNA of murine tissue, 100 bp marker. (B) Treatment regime for Mx1-Cre mediated deletion of Cdk4 (Cdk4Δ/Δ) or Cdk6 (Cdk6Δ/Δ) by polyinosinic–polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C)) injection (200 mg, intraperitoneally, three times every 3 days). (C) Deletion PCR: confirmation of Cdk4Δ/Δ (top) or Cdk6Δ/Δ (bottom) DNA in splenocytes showing wild-type (wt), floxed and delta bands. Analysis was performed 3 weeks post final poly(I:C) injection. (D) Immunoblotting: protein levels of CDK4 and CDK6 in spleen cells (Cdk4fl/fl or Cdk6fl/fl, Cdk4Δ/Δ, Cdk6Δ/Δ, n=3/genotype). α-tubulin served as a loading control. Analysis was performed 3 weeks post final poly(I:C) injection. A representative blot of at least three independent experiments is shown. (E) Quantification of immunoblot shown in (D), signal intensities were normalized to α-tubulin levels (A.U. [arbitrary units]). Cdk4Δ/Δ or Cdk6Δ/Δ protein levels were compared to the respective controls by performing Mann- Whitney U tests.