Figure 1.
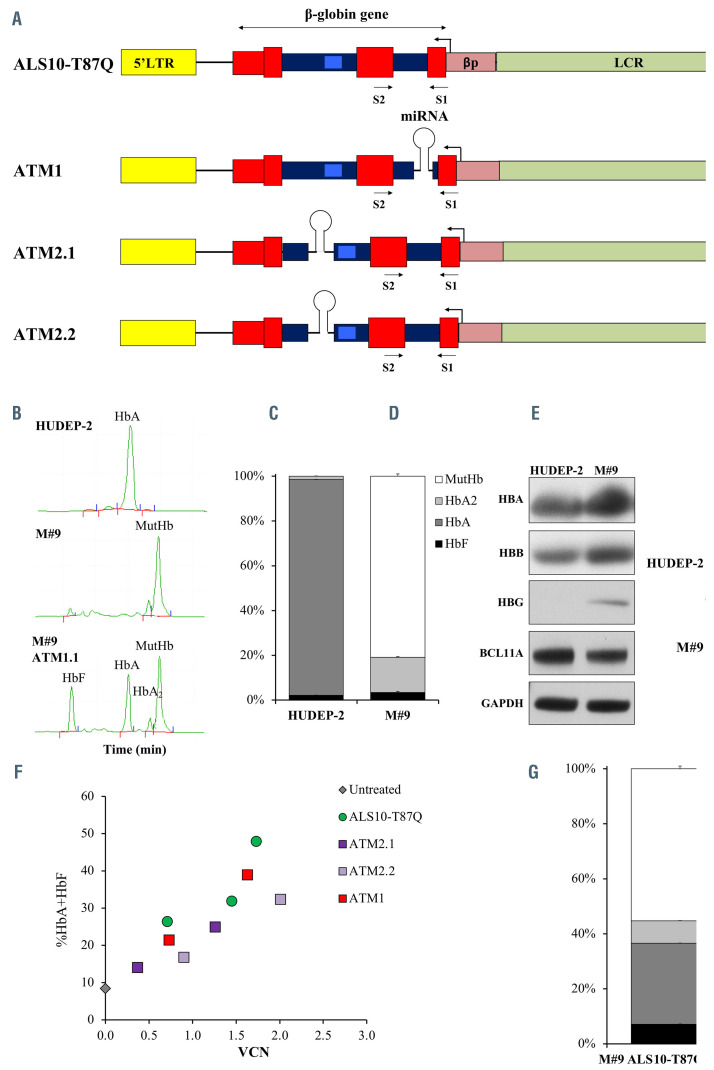
Initial constructs design, Hudep9 (M#9) line development and characterization of constructs efficiency. (A) Initial constructs used in the study: ALS10- T87Q, ATM1.1, ATM2.1, ATM2.2. The miR-E-BCL11A5 sequences were synthesized by Genscript USA (NJ) by combining the passenger and guide sequences of short hairpin RNA (shRNAmiR5) with the flanking miR-E backbone sequences.3,4 The combined miR-E-BCL11A5 sequences were cloned in intron 1 position c.79+36 of ALS10-T87Q (ATM1) and intron 2 positions c.303-163 and c.303-172 (ATM2.1 and ATM2.2, respectively) of the b-globin transgene. Viral production and titration were performed according to methods previously reported.15 All vectors include the human b-globin gene and regulatory elements (β-globin promoter (bp) and portions of the locus control region (LCR) as in our previously described vector AnkT9).8 Some of these vectors present a miRNA as described in the main manuscript. Erythroid specific expression of the b-globin gene and shRNAmiR is achieved by using the b-globin promoter and its locus control region (LCR), in a pol II-promoter driven system. Transgene expression under these regulatory elements will be limited to the latest stages of erythroid development,8 preventing unwanted effects as previously seen in B lymphocytes and hematopoetic stem cellks.10 (B) Representative chromatographic separation (high-performance liquid chromatography [HPLC])2 of hemolysates from the HUDEP-2 (top) and M#9 (middle) erythroblasts (developed using methodology previously described),15 showing fetal hemoglobin (HbF), adult hemoglobin (HbA), HbA2 and mutant HbA (MutHbA) peaks at day 7 of differentiation as described.1,15 At the bottom, a representative chromatographic separation15 of the M#9 cell line after transduction with one of the vectors that simultaneously produced HbAT87Q and induced HbF expression. (C) Relative proportion of HbF, HbA, HbA2 and MutHb in HUDEP-2 and M#9 quantified by HPLC at day 7 of differentiation. (D) Representative western blot showing HBA, HBB, HBG and BCL11A proteins in HUDEP-2 and M#9 at day 7 of differentiation. The evaluation was performed using rabbit anti- HBB (Proteintech, Chicago, Il), rabbit anti-HBA (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), mouse anti-BCL11A (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA) rabbit anti-HBG (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) and rabbit anti-GAPDH (Proteintech) primary antibodies. Secondary, anti-mouse and anti-rabbit IgG HRP-linked antibodies (Cell Signaling) were used for detection with the Amersham enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) western blotting analysis system (GE Healthcare, Malborough, MA, USA). (E) Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots of HUDEP-2 and M#9 stained for GPA, CD71, c-KIT and CD36 markers adapted from and analyzed as previously described.8 (F) Percentage of total curative hemoglobins (HbAT87Q+HbF) over a range of viral integrations after transducing M#9 cells. (G) Proportion of the different hemoglobins produced in M#9 cells transduced with ALS10-T87Q with vector copy number (VCN)= 2.