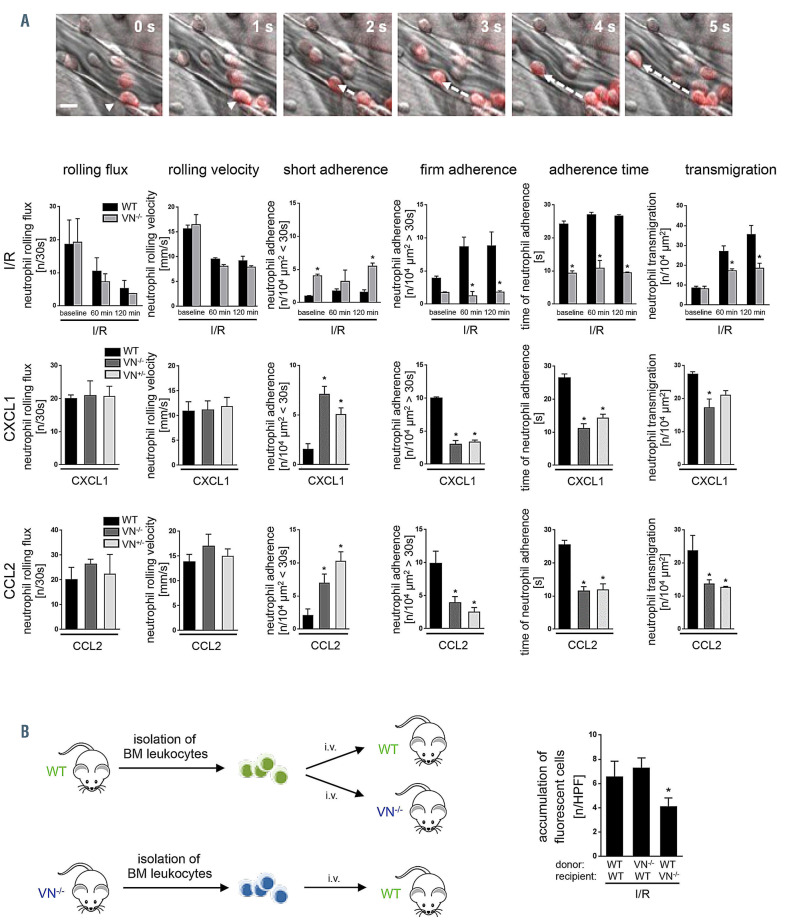
Figure 2.
Role of vitronectin for interactions of neutrophils and endothelial cells. (A) Using multi-channel in vivo microscopy on the inflamed mouse cremaster muscle, interactions of Ly-6G+ neutrophils (red) with endothelial cells were analyzed in postcapillary venules, representative still images are shown (scale bar: 20 mm). Panels show quantitative results for rolling flux, rolling velocity, short adhesion, firm adherence, adhesion time, and transmigration of neutrophils in wild-type (WT), vitronectin (VN)+/-, or VN+/+ mice (mean±standard error of the mean [SEM] for n=4 animals per group; *P<0.05 vs. WT). See also Online Supplementary Table S1. (B) Accumulation of calcein AM-labeled bone marrow (BM) leukocytes were quantified in the postischemic cremaster muscle using multi-channel in vivo fluorescence microscopy. Panel shows results for WT recipient mice receiving leukocytes from WT or VN-deficient donors as well as for VN-deficient recipient mice receiving leukocytes from WT donors (mean±SEM for n=5 animals per group; *P<0.05 vs. WT). n: number; s: seconds; HPF: hydroxyphenyl fluorescein; I/R: ischemia-reperfusion.