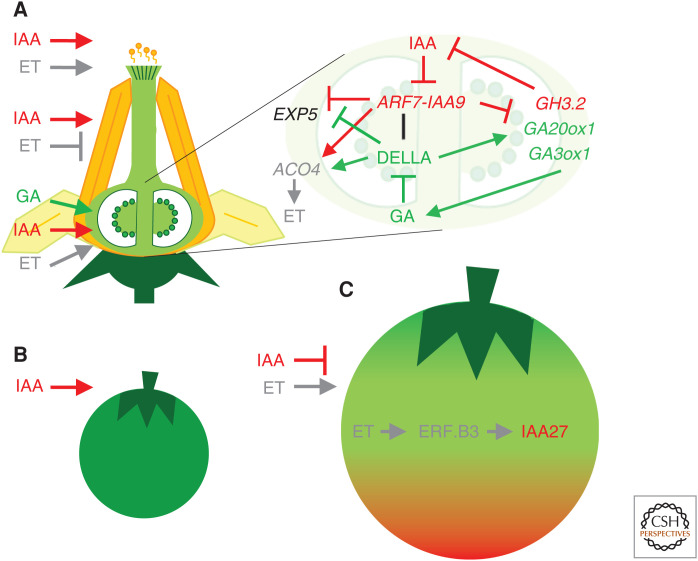
Figure 4.
Auxin interactions with other hormones in fruit development. (A) Hormone interactions in flower development and fruit set. Auxin and ethylene (ET) promote pollen germination and pollen tube growth. Auxin induces and ET represses stamen development. ET positively regulates pistil and ovule development. Auxin and gibberellic acid (GA) promote fruit initiation. (Inset) Molecular network of the hormone crosstalk during tomato fruit initiation. Fertilization triggers auxin-mediated GA synthesis. Auxin inhibits the ARF7-IAA9 complex, releasing the repression of key GA biosynthetic genes. GA–auxin interaction promotes fruit growth by inducing EXP5 and reduces the production of ET by repressing ACO4. (B) Auxin regulates early cell division and fruit development phases. (C) Fruit ripening is promoted by ethylene and repressed by auxin. During ripening, a key molecular interaction between ET and IAA is mediated by ERF.B3 and IAA27. Hormones and their actions are denoted by the following colors: ET is gray, GA is green, and IAA is red. Arrowheads and blunt arrows represent positive and negative regulation.