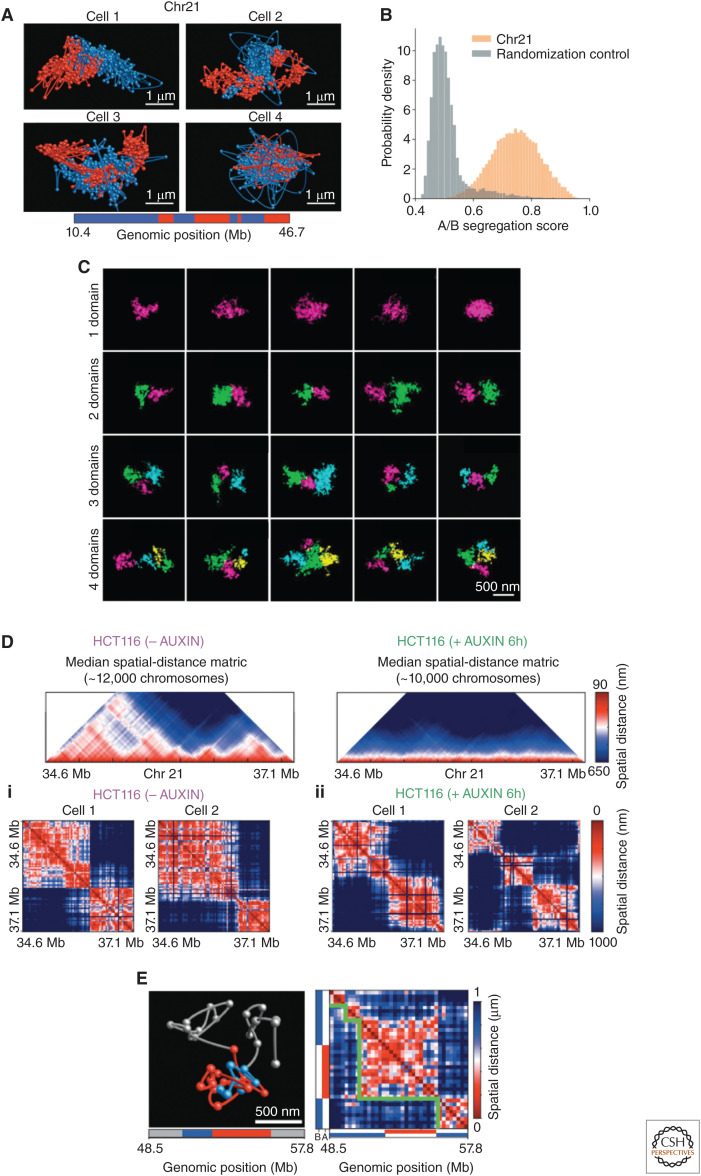
Figure 3.
Chromosome organization varies in single cells. (A) Diverse structures of whole individual chromosomes with the loci that occupy the ensemble-A and -B compartments shown in red and blue. (Panel A from Su et al. 2020; reprinted, with permission, from Elsevier © 2020.) (B) The degree of separation of chromatin for individual chromosomes in the two ensemble-A and -B states compared with a random control. (Panel B from Su et al. 2020; reprinted, with permission, from Elsevier © 2020.) (C) Direct visualization of chromatin with electron microscopy showing the large amount of stochasticity of individual topologically associating domains (TADs)—each assigned domain is color-coded. (Panel C is reprinted from Trzaskoma et al. 2020 under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.) (D) Individual TADs still form in the absence of cohesin. The first row shows the ensemble median distances with (no auxin) and without cohesin (auxin). (Panel D from Bintu et al. 2018; reprinted, with permission, from the American Association for the Advancement of Science © 2018.) (i) TADs in individual cells with cohesion, and (ii) without cohesin. (E) TADs in individual cells can contain loci assigned to the ensemble-A and -B compartments. (Panel E from Su et al. 2020; reprinted, with permission, from Elsevier © 2020.)