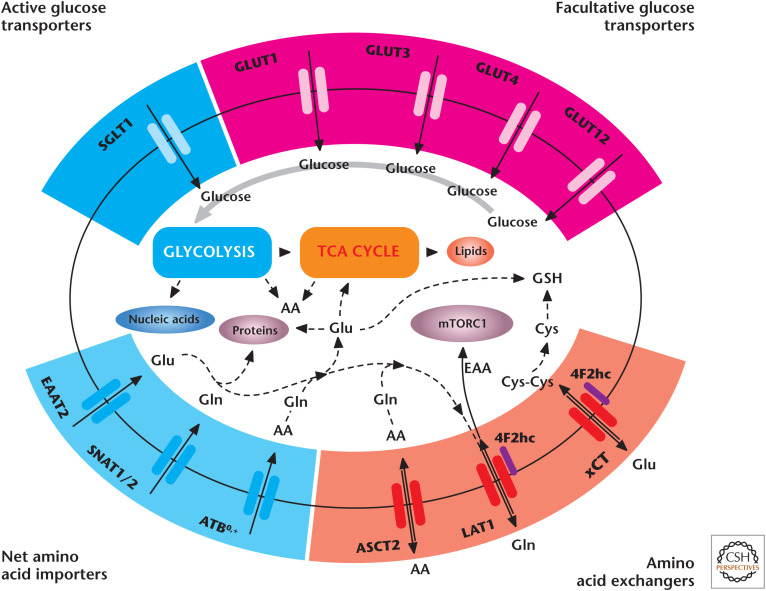
Figure 3.
Cell proliferation requires nutrient transporters. Glucose is imported through SGLTs or GLUTs to fuel glycolysis. Net amino acid transporters, including SNAT1, SNAT2, and ATB0,+, supply glutamine to fuel the TCA cycle and generation of glutamate for GSH synthesis. Glutamine and other amino acids serve as exchange substrates for transporters, such as ASCT2, 4F2hc/LAT1, and 4F2hc/xCT. LAT1 imports EAA to activate mTORC1. Cystine is transported through xCT to support GSH production. AA, amino acid(s); Cys, cysteine; Cys-Cys, cystine; EAA, essential amino acid(s); Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; GLUT, glucose transporter; GSH, glutathione; SGLT, sodium–glucose transporter. (Adapted from McCracken and Edinger 2013, with permission from Elsevier.)