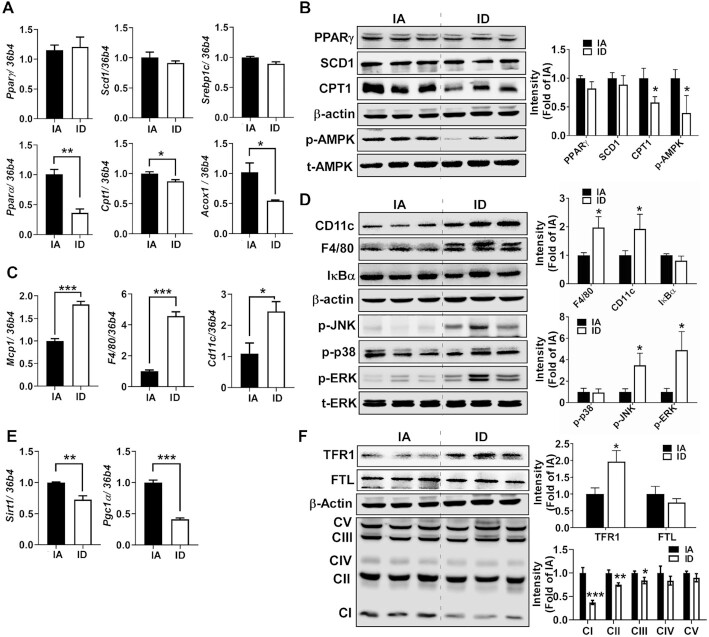
FIGURE 3.
Diet-induced iron deficiency reduces catabolic pathways and promotes inflammation in eWAT. (A) mRNA expression of genes related to lipogenesis (Pparγ, Scd1, and Srebp1c) and fatty acid oxidation (Pparα, Cpt1, and Acox1). (B) Protein expression of lipid metabolism (PPARγ, SCD1, CPT1, p-AMPK, and t-AMPK). (C) mRNA expression of genes related to inflammation (Mcp1, F4/80, and Cd11c). (D) Protein expression of macrophage marker and inflammatory signaling (CD11c, F4/80, IκBα, p-JNK, p-p38, p-ERK, and t-ERK). (E) mRNA expression of genes related to mitochondrial biogenesis (Sirt1 and Pgc1α). (F) Protein patterns of TFR1 (iron importer), FTL (storage iron), and OxPhos. Values are mean ± SD, n = 8. In qPCR analysis, 34b4 was used as a reference gene. In Western blot analysis (n = 6), β-actin was used as a loading control except for t-AMPK and t-ERK to normalize p-AMPK (in B) and p-ERK (in D). Quantitation is shown next to the representative Western blot images. Asterisks indicate the difference from IA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, by Student t test. Acox1, peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1; Cd11c, cluster of differentiation 11c; Cpt1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; FTL, ferritin light; IA, iron adequate; ID, iron deficient; IκBα, NF-κB inhibitor α; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; Mcp1, monocyte chemoattractant protein; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation; Pgc1α, Pparγ coactivator 1α; Pparα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; Pparγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; Scd1, stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1; Sirt1, sirtuin 1; Srebp1c, sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1; TFR1, transferrin receptor 1.