Figure 2.
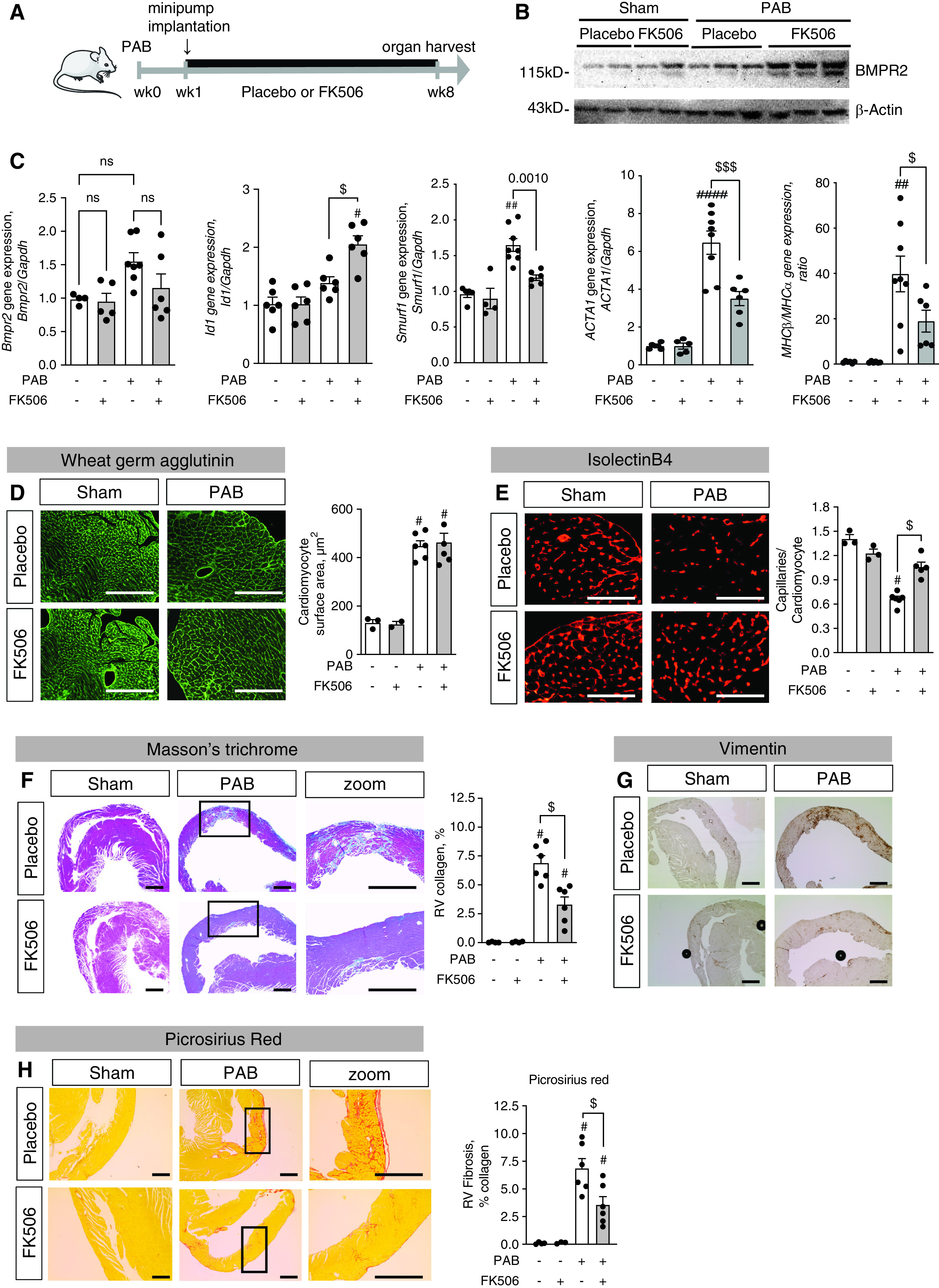
Treatment with FK506 increases BMP signaling, improves RV capillarization, and reduces RV fibrosis under chronic RV pressure overload conditions. (A) Male C57Bl6 mice underwent sham surgery or moderate PAB (around a 24-G needle) and received either placebo or FK506 (0.05 mg/kg/d via osmotic minipump) at Week 1 after surgery for an additional 7 weeks. (B and C) FK506 therapy increased BMPR2 protein expression (B) and Id1, BMPR2, Smurf1 (Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1), Acta1, and MHCβ (myosin heavy chain β)/MHCα (myosin heavy chain α) gene expression in the hypertrophied right ventricle (C). (D) Wheat germ agglutinin staining further revealed PAB-induced RV cardiomyocyte hypertrophy independent from FK506 therapy. (E) Isolectin B4 staining of RV capillaries showed an increased capillary:cardiomyocyte ratio, demonstrating that FK506 preserved the RV vasculature after PAB. (F and G) In addition, Masson’s trichrome staining revealed reduced PAB-induced collagen accumulation in the right ventricle (F) together with reduced vimentin+ fibroblasts (G) when animals received FK506 therapy. (H) Picrosirius red stain confirms collagen accumulation in interstitium n = 3 sham-operated mice per group; n = 6 PAB mice per group. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post hoc test. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ####P < 0.001 versus sham. $P < 0.05 and $$$P < 0.001 versus placebo. Scale bars: F–H, 200 μm; D and E, 100 μm. ns = not significant.
