Figure 6.
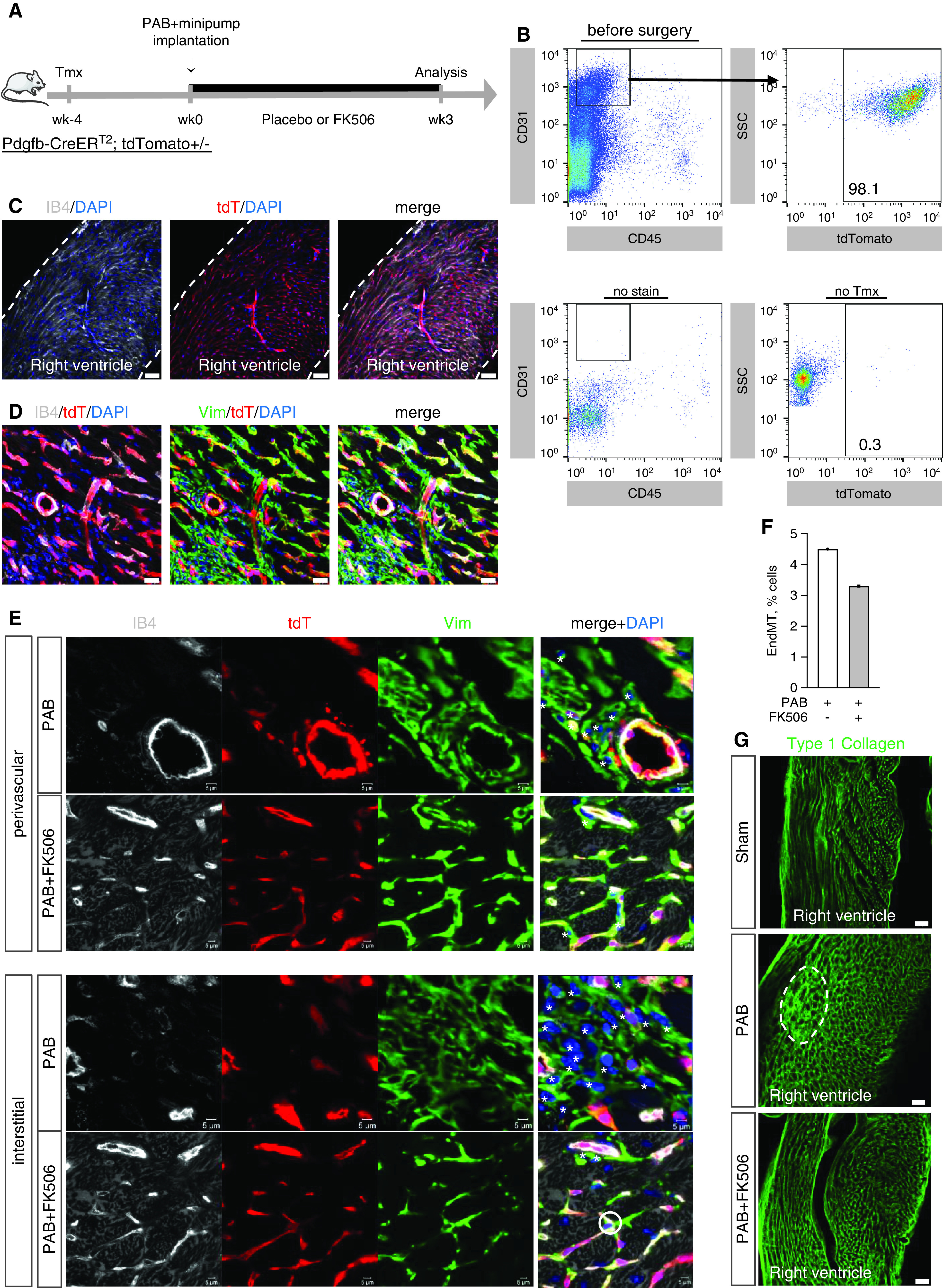
Minority of cardiac endothelial cells transition toward fibroblast-like cells and contribute to pressure overload–induced RV fibrosis, which is reduced by FK506 therapy. Permanent genetic labeling of cardiac endothelial cells and their progeny was performed through tamoxifen (Tmx) administration (2 × 4 mg i.p.) to Pdgfb-CreERT2 mice driving tdTomato (tdT) reporter expression (Week −4). (A) Four weeks after the initial labeling pulse, mice underwent sham surgery or moderate PAB (around 24-G needle) with subsequent placebo or FK505 (0.05 mg/kg/d via osmotic minipump) treatment (Week 0) beginning at the day of surgery for an additional 3 weeks of cell fate chasing. Fluorescent activated cell sorting at the time before surgery revealed tdT reporter labeling in right ventricle endothelial cells (CD31+CD45−), demonstrating efficient endothelial lineage labeling (>98%). (B) Cell gating was defined in control experiments with either lack of CD31 staining (no stain) or lack of tdT labeling (no Tmx). (C) Immunostaining confirmed endothelial IB4 (isolectin B4) costaining with tdT in capillaries and larger blood vessels but neither epicardium nor endocardium (dashed lines), excluding a contribution of epicardial or endocardial cells to EndMT (maximum intensity projections). (D) PAB caused patchy interstitial and perivascular fibrosis with fibroblast (vimentin+ IB4−) accumulation in fibrotic regions within the RV free wall without prevalent tdT colabeling. (E and F) Tissue analysis further revealed that only a minority (<5%) of fibroblasts in interstitial and perivascular fibrotic regions were tdT lineage labeled and derived from an endothelial origin (*: Vim+IB4-tdT-; o: Vim+IB4-tdT+). (G) Type 1 collagen staining demonstrated that patchy collagen accumulation (dashed line) in the PAB-challenged hypertrophic right ventricle is attenuated by preventive administration of FK506. Scale bars: C and G, 50 μm; D, 10 μm; E, 5 μm. EndMT = endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition; SSC = side scatter; Vim = vimentin.
