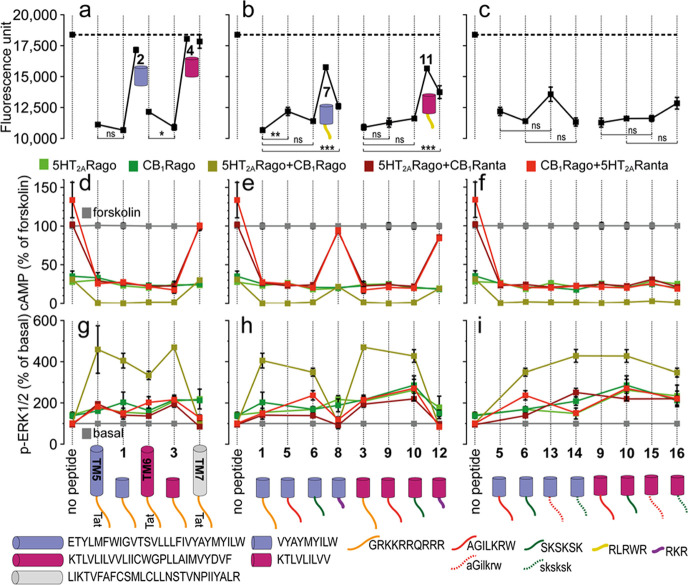
Figure 2.
(a–c) BiFC analysis of the effect of designed peptides on CB1R–5HT2AR heteromerization. Fluorescence (530 nm) of HEK-293T cells transfected with 5HT2AR-cYFP and CB1R-nYFP treated with a vehicle (no peptide) or 4 μM peptide for 4 h. Values are mean ± SEM of n = 10–30; TM5-Tat and Tat-TM6 are positive controls, whereas TM7-Tat is a negative control; ns (no significant), *(p < 0.05), **(p < 0.01), and ***(p < 0.001) represent significantly different (two-tailed) values (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests). (d–i) Effect of designed peptides on the decrease in FK-induced cAMP (d–f) or increase in ERK1/2 phosphorylation. (g–i) Transfected cells preincubated with a vehicle (no peptide) or with 5HT2AR (5HT2ARago, DOI, 100 nM) or CB1R (CB1Rago, WIN, 100 nM) agonists or with 5HT2AR (5HT2ARanta, MDL, 300 nM) or CB1R (CB1Ranta, RIM, 1 μM) antagonists and combinations thereof, in the presence or absence of 0.5 μM FK. Values in panels (d–f) are mean ± SEM of n = 3–6 of FK-treated cells. Quantification of phosphorylated ERK-1/2 was determined by the α-screen bead-based technology. Values in panels (g–i), expressed as a percentage of basal (nontreated cells), are mean ± SEM of n = 4–9. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests was used to analyze the data (Table S5). Cartoons depict the designed peptides (cylinders with color codes as in Figure 1) fused to different CPPs (lines).