Figure 1.
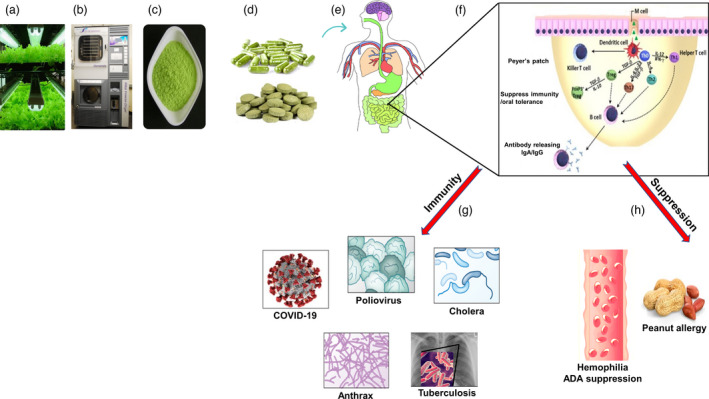
Mechanism of oral drug delivery and examples of chloroplast therapeutics and booster vaccines. (a) The cGMP growing facility for lettuce leaf biomass production. (b) The lyophilizer that dehydrates lettuce biomass through optimized programming for freeze‐drying. (c) Optimized grinding to maintain the intactness of plant cells. (d) The capsule/gum preparation maintaining antigen stability. (e) The oral delivery of proteins bioencapsulated in plant cells. (f) Mechanism of immune suppression/tolerance or conferring immunity. GM1 ganglioside receptors on intestinal epithelial cells facilitate uptake CTB‐fused proteins. DCs are antigen‐presenting cells, induce antigen‐specific T and B cells. The IFN‐γ and Th2 cytokines (IL‐4, IL‐10) are critical for cell‐mediated and humoral immunity. After TGF‐β production, FoxP3+ Treg cells are induced by DCs. The immune tolerance via induction and maintenance of FoxP3+ Treg cells is mediated by TGF‐β. (g) Examples of potential chloroplast‐derived booster vaccines against viral (polio, COVID‐19) and bacterial (anthrax, cholera, tuberculosis) diseases. (h) Oral tolerance induction and immune suppression in haemophilia and the prevention of peanut allergy.
