Figure 3.
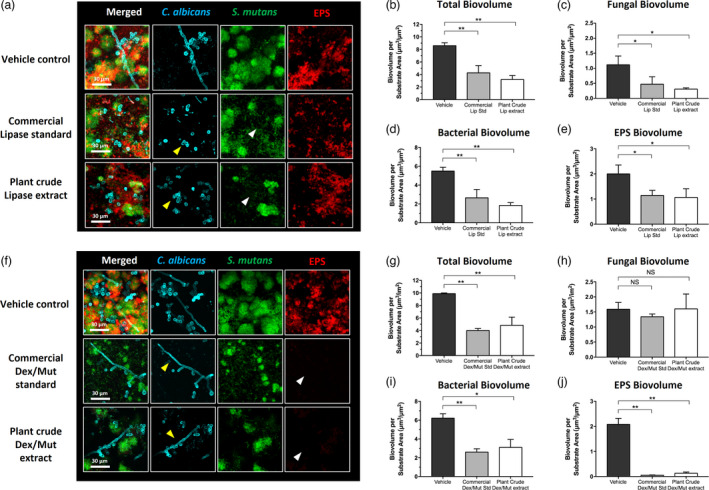
Antibiofilm effects of commercial and plant‐derived enzymes against bacterial‐fungal mixed biofilms. Commercial purified enzymes of the same activity unit as measured in the plant crude extracts (333.3 U/mL for lipase and 7.08/0.84 U/mL for dextranase/mutanase, respectively) were used as standards to evaluate the antibiofilm efficacy of the plant crude extracts. (a) Confocal images showing the antibiofilm efficacy of commercial and plant‐derived lipase. (b–e) Quantitative computational analysis of the confocal biofilm images treated with commercial and plant‐derived lipase. (f) Confocal images showing the antibiofilm efficacy of commercial and plant‐derived Dextranase/Mutanase combination. (g–j) Quantitative computational analysis of the confocal biofilm images treated with commercial and plant‐derived Dextranase/Mutanase combination. For multi‐channel confocal images, C. albicans cells (yeasts or hyphae) are depicted in cyan; S. mutans cells are depicted in green; The EPS glucan matrix is depicted in red. For the computational data, the title of each graph indicates the channel(s) used for individual analysis. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (one‐way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). Enzyme units of lipase and dextranase/mutanase represent µmol of pNP and reducing sugar produced in 1 h, respectively.
