Figure 2. LRRK2 phosphorylates AP2M1 in vitro and in vivo.
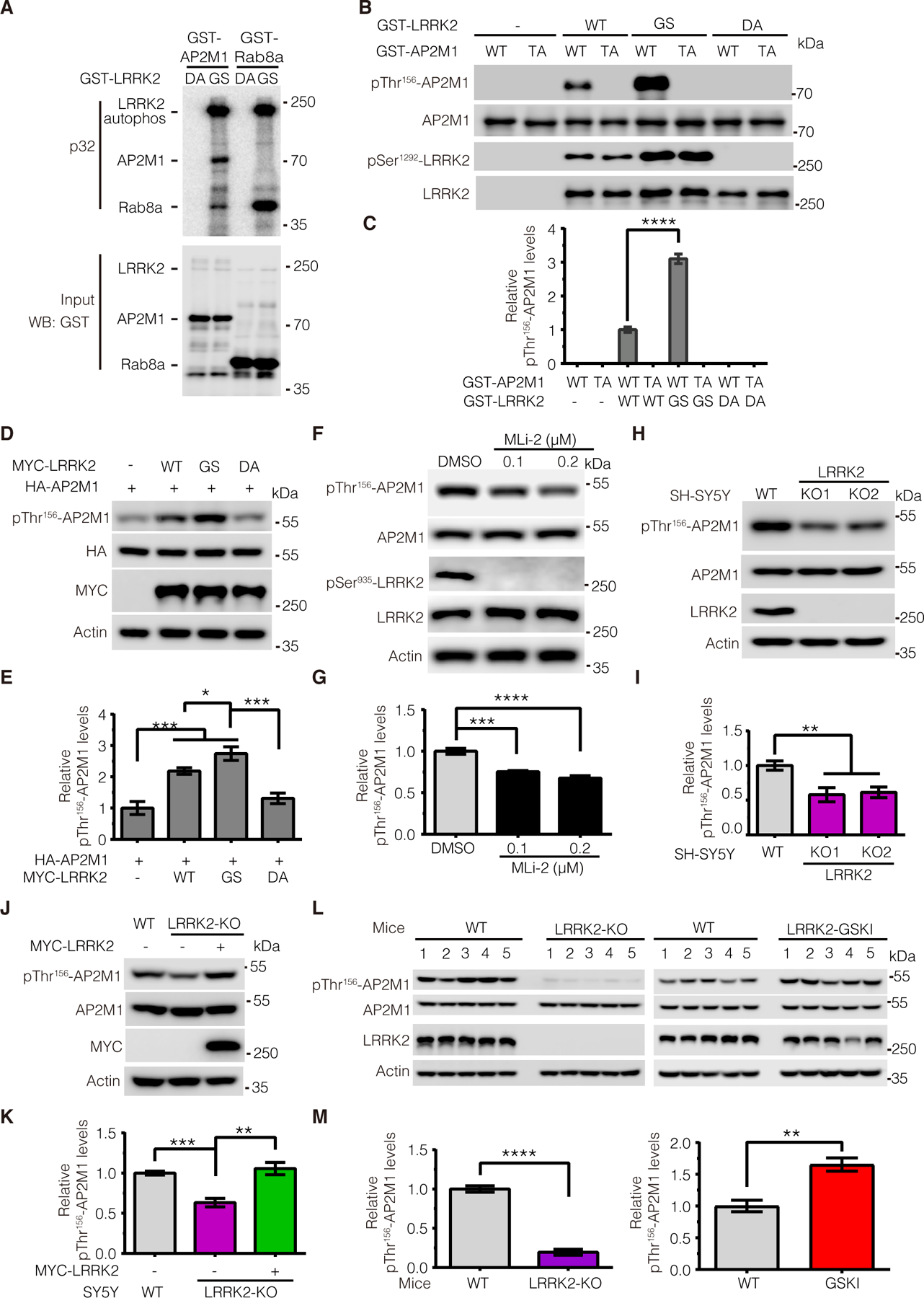
(A) In vitro kinase assays assessing the amount of 32P-ATP incorporated by GST-tagged AP2M1 upon incubation with recombinant GST-tagged LRRK2 protein—either the PD-associated G2019S (GS) mutant or the kinase-deficient D1994A (DA; 970–2527aa) mutant. Rab8a was as a positive control. (B and C) In vitro kinase assays assessing phosphorylation of recombinant GST-tagged WT or phospho-deficient T156A (TA) mutant AP2M1 by recombinant GST-tagged WT, GS mutant, or DA mutant LRRK2. Immunoblots were performed with antibody to pThr156-AP2M1. (D and E) Immunoblotting analysis of AP2M1 phosphorylation at Thr156 upon overexpression of WT, GS mutant, or DA-mutant LRRK2. (F and G) Immunoblotting analysis of endogenous AP2M1 phosphorylation level at Thr156 upon MLi-2 inhibitor treatment. Lysates from SH-SY5Y cells treated with MLi-2 (0.1 or 0.2 μM for 2 hours) were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies to pThr156-AP2M1 and pSer935-LRRK2. (H and I) Immunoblotting analysis of endogenous AP2M1 phosphorylation at Thr156 in WT and LRRK2-KO SH-SY5Y cells. (J and K) Immunoblotting analysis of endogenous AP2M1 phosphorylation at Thr156 upon overexpression of MYC-LRRK2 in LRRK2 KO cells. (L and M) Immunoblotting analysis of endogenous AP2M1 phosphorylation at Thr156 in brain tissue from WT, LRRK2 knockout (KO), and LRRK2 G2019S-knock-in (GSKI) mice. Images were quantified by ImageJ software. All quantification data are mean ± SEM from n=5 independent experiments or mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by Student’s t tests for two comparisons or one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s post hoc test for multiple comparisons.
