Fig. 1.
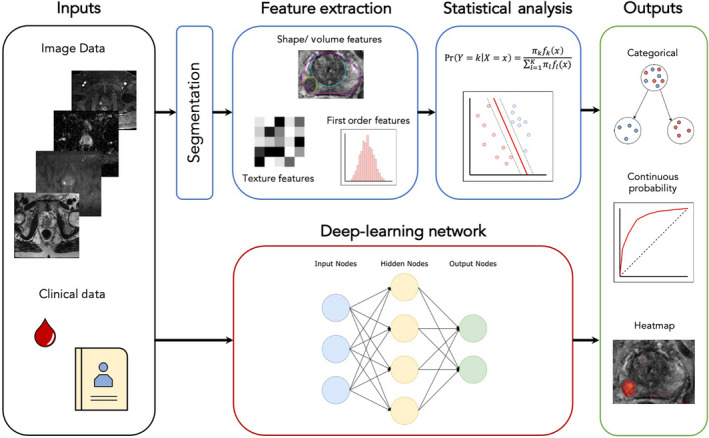
Schematic diagram of common approaches to ML in medical imaging, from left to right. Inputs (black box) often include imaging DICOM (digital imaging and communications in medicine) data and clinical data. For classical ML (blue boxes), images are often segmented and radiomic features extracted for input into the chosen statistical analysis, whereas, for DL methods (red box), the neuronal network uses often unknown discriminating features found during training to classify patients into a specified output (green box), which could be a categorical group or a continuous probability where a receiver operating curve may be produced and, if analysis is done on a voxel‐by‐voxel basis, a heatmap can be constructed.
